Diabetes is a complex chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose, leading to high blood sugar levels. While diabetes can impact individuals of any gender, there are specific signs, symptoms, and complications that are unique to women. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of diabetes in women, including types of diabetes, common symptoms, specific signs and symptoms, fertility-related issues, and potential complications.
Types of Diabetes:
1.Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to a lack of insulin production. It is commonly diagnosed in children and young adults.
(For more information on type 1 diabetes symptoms.)
2.Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. Lifestyle factors such as obesity and lack of physical activity play a significant role in its development.
3.Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and child.
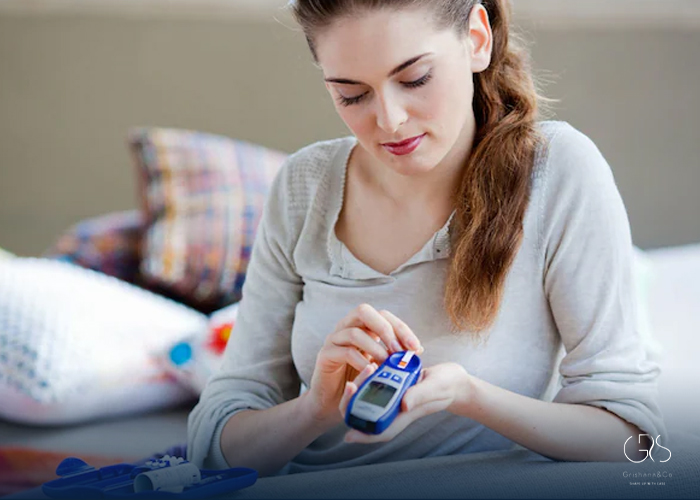
Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow wound healing
Signs and Symptoms in Females:
- Vaginal Dryness: High blood sugar levels can cause vaginal dryness, leading to discomfort during sexual intercourse and an increased risk of vaginal infections.
- Genitourinary Infections: Women with diabetes are more prone to genitourinary infections such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), recurrent vaginal yeast infections, and bacterial vaginosis.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Diabetes can affect hormone levels and lead to irregular menstrual cycles or the development of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by hormonal imbalances and ovarian cysts.
- Infertility: Women with diabetes may face challenges with fertility due to hormonal imbalances and irregularities in ovulation.
(For more information on type 1 diabetes symptoms.)

Complications Women and Children are at Higher Risk of:
- Pregnancy Complications: Women with diabetes are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy, such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or delivering larger babies.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): This life-threatening complication can occur in individuals with type 1 diabetes, particularly when blood sugar levels are uncontrolled.
- Symptoms in Children: Children with diabetes may exhibit symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, irritability, and fatigue.
- Symptoms in Men: Similar to women, men with diabetes may experience common symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurry vision.
- Is Diabetes Contagious? Diabetes is not a contagious disease; it is primarily influenced by genetic and lifestyle factors.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider:
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early detection, proper management, and lifestyle modifications can help prevent complications and improve quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Conclusion:
In summary, diabetes presents unique challenges for women, impacting various aspects of their health, including reproductive health, urinary tract health, and overall wellbeing. By staying informed, proactive, and collaborating closely with healthcare providers, women can effectively manage their diabetes, reduce the risk of complications, and strive for optimal health and wellness.
Sources
- CDC, Diabetes and Women
- Mayo Clinic, Gestational Diabetes
- Healthline, How Diabetes Affects Women
- American Diabetes Association, Gestational Diabetes