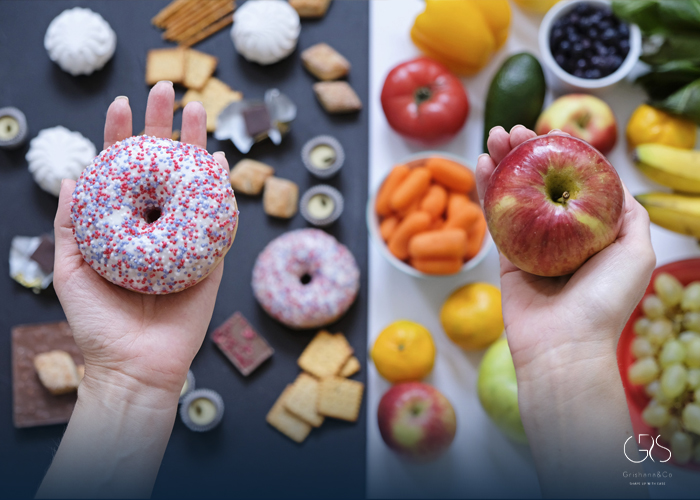
When it comes to cancer prevention, the impact of diet cannot be underestimated. Genetics and environmental factors certainly contribute to the development of cancer, but incorporating the right foods into your diet can significantly reduce the risk. Scientific research has identified specific compounds in certain foods that have the potential to lower the risk of cancer. By incorporating these cancer-fighting foods into your daily routine, you can take a proactive and effective approach towards reducing your risk of developing this life-threatening disease. Don’t underestimate the power of food in mitigating Food and Cancer Risk and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Foods That May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
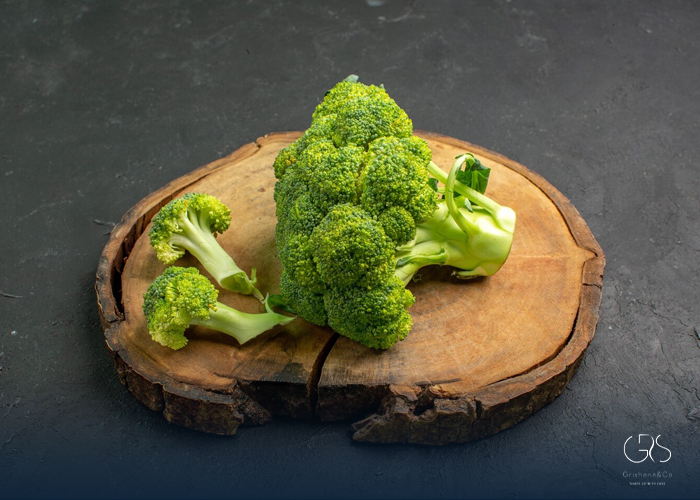
Broccoli: A cruciferous vegetable containing sulforaphane, known for its anti-cancer properties. Studies suggest that sulforaphane can inhibit cancer cell growth, lowering the risk of breast and prostate cancer.
(If you’re interested in learning about broccoli types , I suggest checking out this informative article.)

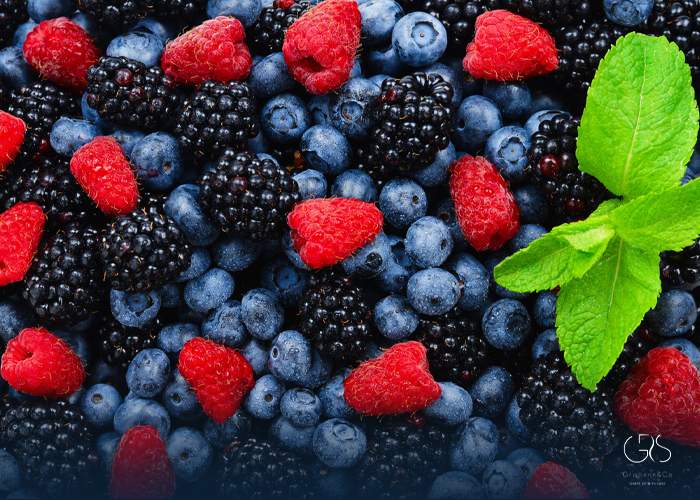
Berries: Rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals, berries, such as blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries, can reduce inflammation, protect cells, and potentially decrease the risk of cancer development.
(Check out my article on the benefits of blueberries)

Garlic: Contains organosulfur compounds with anti-cancer properties. Garlic may inhibit cancer cell growth, particularly in colorectal cancer.
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, an anti-inflammatory compound with antioxidant properties. Research supports curcumin’s potential in reducing cancer cell growth.
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in folate, fiber, and carotenoids, offering protection against various cancers, including lung and stomach cancer.
Green Tea: Rich in catechins, green tea consumption is associated with a lower risk of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer due to its antioxidant properties.
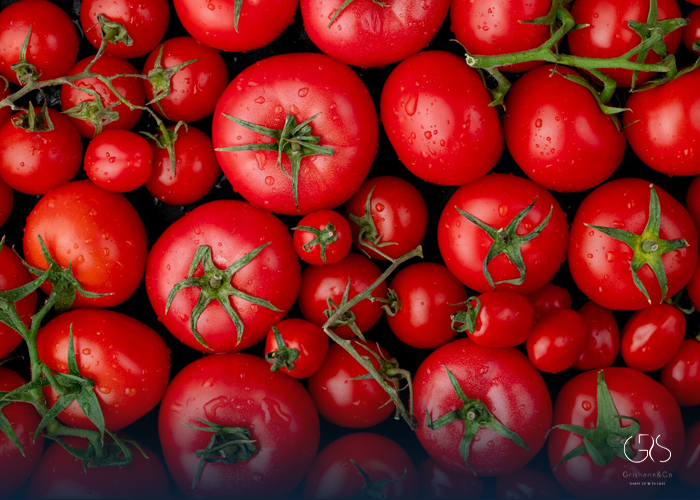
Tomatoes: Lycopene in tomatoes has antioxidant properties that protect cells from damage and potentially inhibit cancer cell growth, lowering the risk of cancer.

Nuts and Seeds: Associated with a reduced risk of pancreatic and colorectal cancer, nuts and seeds are packed with nutrients and healthy fats that support overall health.
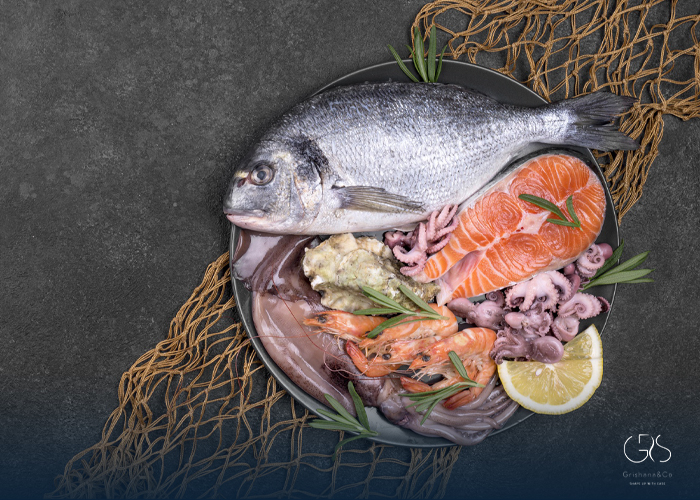
Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines contain omega-3 fatty acids known for their anti-inflammatory properties, potentially reducing the risk of breast and prostate cancer.

Foods to Limit or Avoid
1.Processed and Red Meats: Consumption of processed meats and red meats has been linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Limiting the intake of these meats can reduce cancer risk.
2.Sugary Drinks and Snacks: High consumption of sugary beverages and snacks has been associated with obesity and an increased risk of certain cancers, such as liver and colorectal cancer. Limiting these items can lower cancer risk.
3.Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption is a risk factor for various cancers, such as breast, liver, and esophageal cancer. Moderation or avoidance of alcohol is advisable to reduce cancer risk.
Diets that Help Prevent Cancer
1.Mediterranean Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil and nuts, the Mediterranean diet is associated with a reduced risk of cancer, particularly colorectal and breast cancer.
2.Plant-Based Diet: A diet focused on plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes has been linked to a lower risk of cancer due to its high fiber and antioxidant content.
3.Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Emphasizing foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and fatty fish, the anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce inflammation in the body, lowering the risk of cancer development.
Conclusion:
Prioritizing cancer-fighting foods and adhering to dietary guidelines significantly contributes to a healthier lifestyle, minimizing the risk of cancer. By incorporating a well-balanced diet rich in cruciferous vegetables, berries, garlic, turmeric, leafy greens, green tea, tomatoes, nuts and seeds, as well as fatty fish, you can potentially lower your chances of developing cancer. Conversely, it is vital to limit the consumption of processed and red meats, sugary drinks and snacks, and excessive alcohol intake, as these have been linked to increased cancer risk. Furthermore, following specific diets like the Mediterranean, plant-based, or anti-inflammatory diets can offer added protection against cancer. However, seeking personalized advice from healthcare professionals is crucial to determine effective strategies for reducing Food and Cancer Risk that align with your individual needs.
Sources
- American Cancer Society, Diet and Physical Activity: What’s the Cancer Connection?
- National Cancer Institute, Cancer Prevention Overview (PDQ®) - Patient Version
- World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF), Diet, activity and cancer
- American Institute for Cancer Research, Cancer Prevention Recommendations