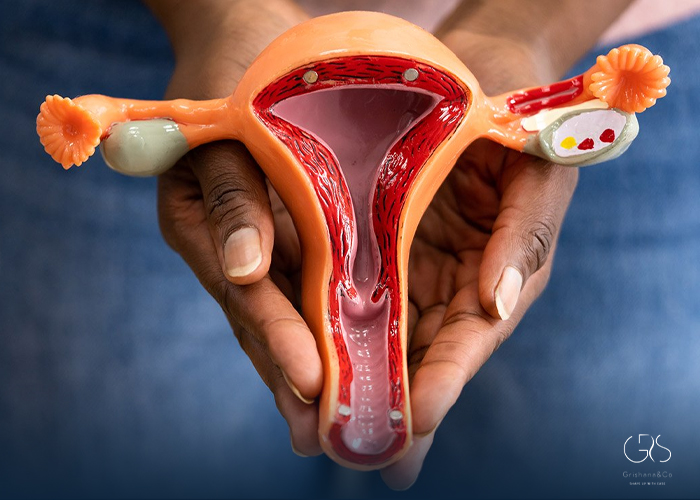
Ovarian cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease that affects thousands of women around the world each year. In the United States, it is estimated that around 21,750 new cases of ovarian cancer will be diagnosed in 2020, with approximately 13,940 deaths attributed to this disease (“Ovarian Cancer Statistics”). The key to improving the prognosis for women with ovarian cancer lies in early detection. By recognizing the early signs of ovarian cancer, individuals can seek medical help sooner and increase the likelihood of successful treatment. This article aims to shed light on 8 early signs of ovarian cancer, while also considering diverse perspectives and including relevant statistical data.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, which are two small organs located on either side of the uterus in the female reproductive system. It often goes undetected until it has spread within the pelvis and abdomen. This is one of the main reasons why ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage. However, there are early warning signs that, if recognized, can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
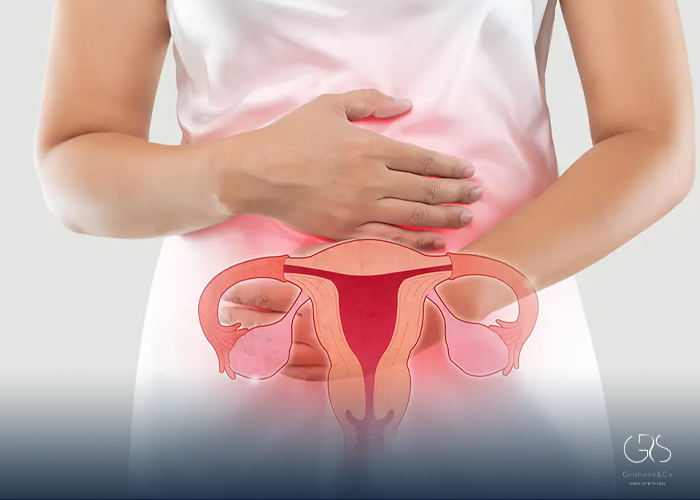
8 Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer
- Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis is a common symptom of ovarian cancer. It may feel like a dull ache, a sharp pain, or a general discomfort.

- Bloating: Feeling bloated, or experiencing pressure or pain in the abdomen, can be an early sign of ovarian cancer. This bloating may be constant or come and go.
- Difficulty Eating or Feeling Full Quickly: Women with ovarian cancer often report a loss of appetite or feeling full sooner than usual after eating. This is known as early satiety.
- Urinary Symptoms: Frequent and urgent urination, as well as ongoing discomfort when urinating, can be indications of ovarian cancer.
- Change in Bowel Habits: Sudden changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea, that persist for more than a few days could be a sign of ovarian cancer.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain: A significant, unexplained weight loss or gain can be a warning sign of various types of cancer, including ovarian cancer.

- Fatigue: While fatigue is a common symptom of many conditions, persistent fatigue that is not relieved by rest could be an early sign of ovarian cancer.

- Changes in Menstrual Cycle: Unusual changes in the menstrual cycle, including abnormal bleeding or spotting, should be discussed with a doctor and may warrant further investigation.
It is important to note that these symptoms can be caused by conditions other than ovarian cancer. However, if any of these signs are persistent and do not go away, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Diverse Perspectives on Ovarian Cancer Awareness
The impact of ovarian cancer is not limited to a particular demographic or community, and it is important to consider diverse perspectives when discussing awareness and early detection. A lack of awareness and resources in certain communities can lead to delayed diagnosis and poorer outcomes for women with ovarian cancer.
In underserved communities or among certain demographic groups, there may be cultural or socioeconomic barriers to accessing healthcare. Language barriers, lack of health insurance, and mistrust of the medical system can all contribute to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, there may be stigma surrounding gynecological health in some cultures, leading to reluctance in seeking medical care for symptoms such as those associated with ovarian cancer.
It is essential to address these disparities by promoting education and awareness about ovarian cancer in diverse communities. This includes providing culturally sensitive information about the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer, as well as increasing access to screening and diagnostic services in underserved areas. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by different communities, healthcare providers and organizations can work towards improving early detection and treatment outcomes for all women.
Relevant Statistical Data
When it comes to ovarian cancer, understanding the relevant statistical data is crucial for raising awareness and advocating for improved screening and early detection efforts. In the United States, the American Cancer Society estimates that about 1 in 78 women will develop ovarian cancer in their lifetime (“Ovarian Cancer Statistics”). The average age at which ovarian cancer is diagnosed is 63, and it is more common in white women than in women of other races or ethnicities.
However, it is important to note that these statistics do not fully capture the impact of ovarian cancer on diverse communities. There are disparities in ovarian cancer outcomes based on factors such as race, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare. For example, African American women have a lower incidence of ovarian cancer but a higher mortality rate compared to white women. This underscores the importance of addressing disparities in ovarian cancer awareness and access to care, particularly in marginalized communities.
Improving access to healthcare, advocating for increased funding for ovarian cancer research, and promoting diversity in clinical trials are all essential steps towards reducing disparities in ovarian cancer outcomes. Additionally, ongoing efforts to raise awareness about the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer in diverse communities can help facilitate earlier diagnosis and improved treatment outcomes for all women.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of ovarian cancer is a pivotal step in improving outcomes for women affected by this disease. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can contribute to early diagnosis and effective treatment. It is also crucial to consider diverse perspectives and address disparities in ovarian cancer awareness and access to care. Through education, advocacy, and improved resources, we can work towards ensuring that all women have the opportunity for early detection and better outcomes in the fight against ovarian cancer.
Sources
- American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Ovarian Cancer
- National Ovarian Cancer Coalition, Shine a Light on Ovarian Cancer
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Ovarian Cancer Statistics