Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood, which can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly. One of the key components of managing type 2 diabetes is regular exercise. Exercise has been shown to play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. In this article, we will explore the best ways to exercise for individuals with type 2 diabetes, including the benefits of post-meal and evening workouts, the importance of mixing up exercise activities, and using exercise to break insulin barriers.
Using Exercise to Regulate Type 2 Diabetes
According to the American Diabetes Association, regular physical activity is a crucial component of managing type 2 diabetes. Engaging in regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and manage weight, all of which are important factors in managing type 2 diabetes. In fact, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that individuals with type 2 diabetes who engaged in regular exercise had better glycemic control and reduced cardiovascular risk factors.
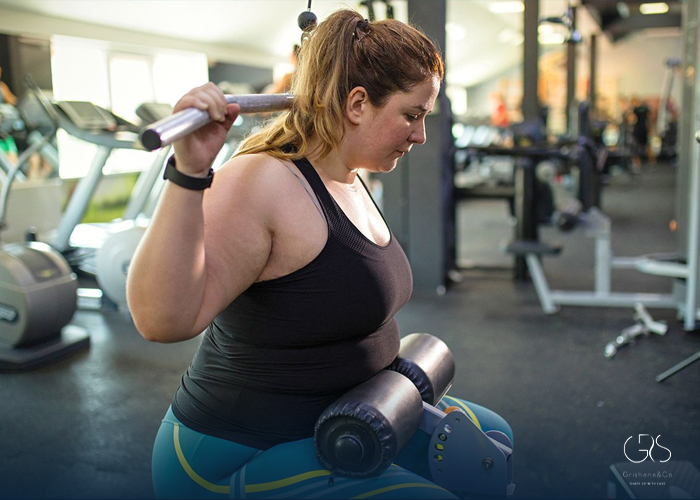

Post-Meal and Evening Workouts Are Best
Research has shown that post-meal and evening workouts may be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. A study published in Diabetes Care found that a short bout of moderate-intensity walking after each meal resulted in improved overall blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. This is because physical activity helps the body to use up the glucose in the bloodstream more efficiently, thereby reducing post-meal blood sugar spikes. Additionally, exercising in the evening can help improve insulin sensitivity, as the body’s response to insulin is typically lower in the evening.
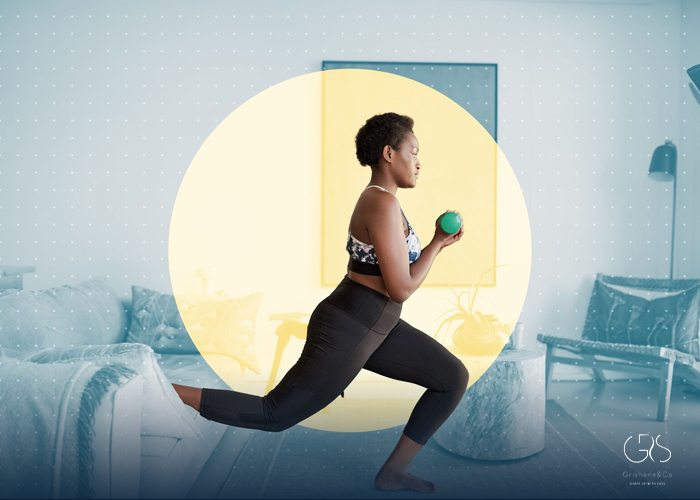

Mixing Up Kinds of Exercise Activities Can Help
It is important for individuals with type 2 diabetes to engage in a variety of exercise activities to reap the maximum benefits. Cardiovascular activities, such as walking, swimming, and cycling, can help improve heart health and promote weight management. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance band workouts, can help increase muscle mass and improve insulin sensitivity. A study published in the journal Diabetologia found that combining aerobic and resistance training had a synergistic effect on glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, mixing up different kinds of exercise activities can help individuals with type 2 diabetes achieve more comprehensive health benefits.
Using Exercise to Break Insulin Barriers
Insulin resistance is a common issue for individuals with type 2 diabetes, making it difficult for the body to utilize insulin effectively. However, exercise has been shown to help break insulin barriers by improving insulin sensitivity. A meta-analysis published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that both aerobic and resistance exercise are effective in improving insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity can help the body’s cells become more responsive to insulin, thereby improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of complications associated with type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes. Post-meal and evening workouts have been shown to be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as they can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Mixing up different kinds of exercise activities can help individuals achieve comprehensive health benefits, including improved heart health, weight management, and insulin sensitivity. By incorporating regular exercise into their routine, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Sources
- American Diabetes Association, Regular exercise can help put you in control of your life.
- National Library of Medicine, Effects of aerobic and resistance training on hemoglobin A1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
- National Library of Medicine, Postprandial walking is better for lowering the glycemic effect of dinner than pre-dinner exercise in type 2 diabetic individuals