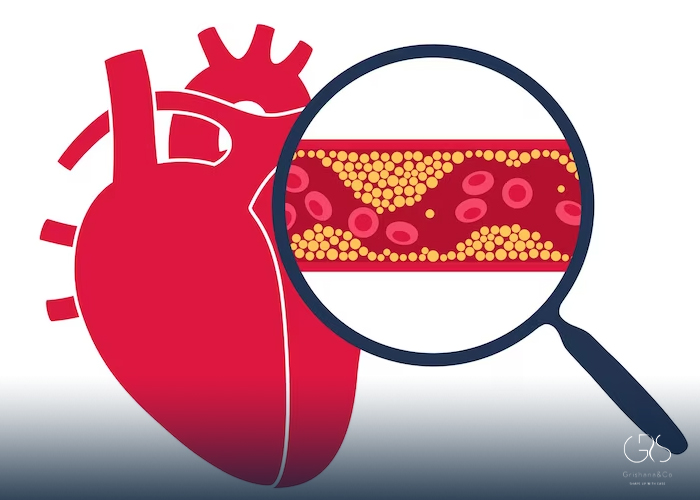
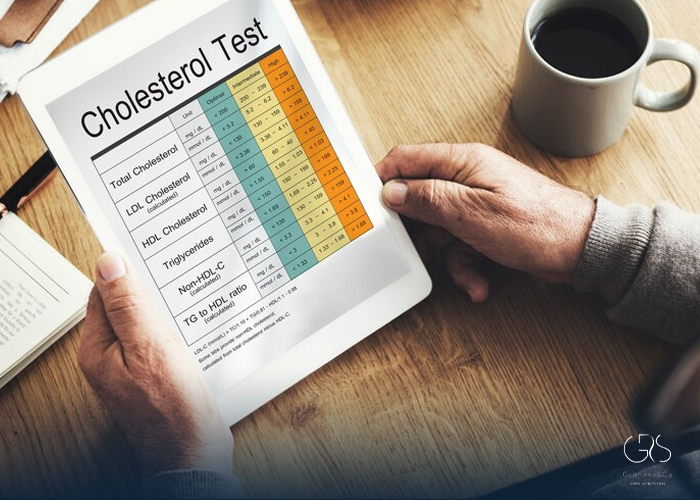
High cholesterol, also known as hyperlipidemia, is a prevalent health issue affecting millions of individuals worldwide. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Understanding how high cholesterol is treated is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps in managing this condition effectively and improving their overall health outcomes.
What is High Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in the blood. While our bodies need cholesterol to function properly and produce essential hormones, having high levels of cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and related complications. High cholesterol often does not cause any symptoms, making regular screenings essential for early detection and intervention.
Treatment Strategies for High Cholesterol
Managing high cholesterol involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medications, and sometimes, nutritional supplements. Below, we delve into these treatment strategies in detail:
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Healthy Diet: A cornerstone of managing high cholesterol is adopting a heart-healthy diet. This entails reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods. Instead, focusing on consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help lower cholesterol levels.

- Physical Activity: Regular exercise plays a crucial role in lowering cholesterol levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week can improve lipid profiles and overall cardiovascular health (source).
(I suggest reading my article to learn more about the benefits of aerobic exercise.)
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise plays a crucial role in lowering cholesterol levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week can improve lipid profiles and overall cardiovascular health (source).

- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is vital for managing high cholesterol and reducing the risk of heart disease. Smoking can lower levels of HDL (good) cholesterol and damage blood vessels, thereby exacerbating the effects of high cholesterol.

Medications:
- Statins: Statins are the most commonly prescribed medications for high cholesterol. They work by blocking the enzyme responsible for producing cholesterol in the liver, thereby lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. Statins have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in individuals with high cholesterol.
- Other Medications: In cases where statins are not effective or tolerated, healthcare providers may prescribe other medications such as bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, or cholesterol absorption inhibitors to manage cholesterol levels.
Nutritional Supplements
- Fish Oil: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil supplements have been shown to have a positive impact on cholesterol levels. They can reduce triglycerides and lower the risk of heart disease, particularly in individuals with high triglyceride levels (source).
- Plant Sterols: Plant sterols, found naturally in certain plant foods, are known to block the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines. Consuming plant sterol-fortified foods or supplements can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Prevention Strategies for High Cholesterol
Preventing high cholesterol is key to reducing the burden of cardiovascular diseases. Here are some effective strategies for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels:
- Regular Health Screenings: Routine cholesterol screenings can help identify high cholesterol early and enable timely intervention to lower cholesterol levels and mitigate associated risks.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Embracing a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep can contribute to maintaining optimal cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular well-being.
- Education and Awareness: Enhancing public awareness about the importance of cholesterol management and promoting healthy lifestyle habits can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Conclusion:
The management of high cholesterol requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle modifications, medication when necessary, and nutritional supplements in some cases. By addressing high cholesterol through a holistic lens, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of cardiovascular diseases and lead healthier lives. Prevention strategies play a critical role in maintaining optimal cholesterol levels and should be integral to public health initiatives.
Sources
- American Heart Association, Prevention and Treatment of High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia)
- Mayo Clinic, High cholesterol