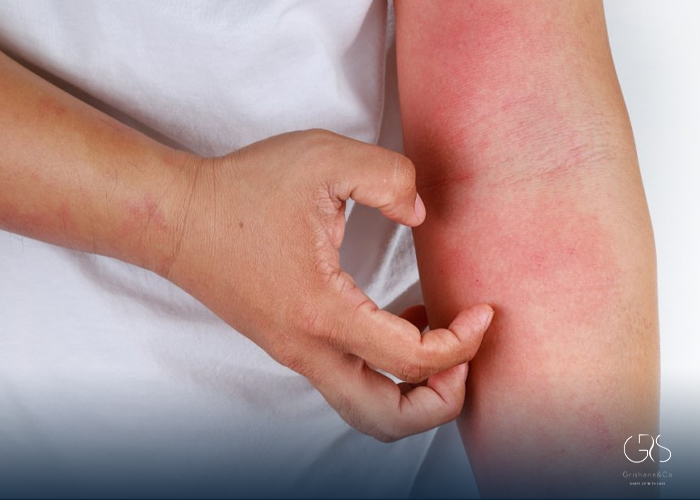
Anaphylactic shock, also known as anaphylaxis, is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that affects multiple systems in the body. It is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anaphylactic shock is crucial for individuals at risk, healthcare professionals, and society at large.
Statistics on Anaphylactic Shock
Anaphylactic shock can occur in individuals of any age group, regardless of previous medical history or allergies. The prevalence rates of anaphylactic shock vary across populations and regions. Understanding these statistics helps to gauge the impact of anaphylactic shock and its significance as a public health concern. Here are some relevant statistics:
- Prevalence: The estimated prevalence of anaphylactic reactions ranges from 1.6% to 5% of the general population.
- Epinephrine Administration: Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis. A study revealed that only 30% of patients experiencing anaphylaxis receive epinephrine before arrival at the emergency department.
- Fatalities: Anaphylaxis-related fatalities are rare, but they can occur. In the United States, it accounts for about 1,500 deaths annually.
Causes and Symptoms
Anaphylactic shock occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to an allergen, resulting in the release of various chemical mediators that cause a rapid and severe response. Common triggers include certain foods (e.g., peanuts, shellfish), insect stings, medications (e.g., antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), latex, and even exercise.
The symptoms of anaphylactic shock can develop within seconds to minutes after exposure to the allergen and may include:
- Skin reactions: Itching, hives, flushing, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Respiratory symptoms: Wheezing, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing.
- Cardiovascular symptoms: Rapid or irregular heartbeat, low blood pressure, or fainting.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
Prompt recognition of these symptoms is crucial for the early administration of epinephrine and prompt medical management.
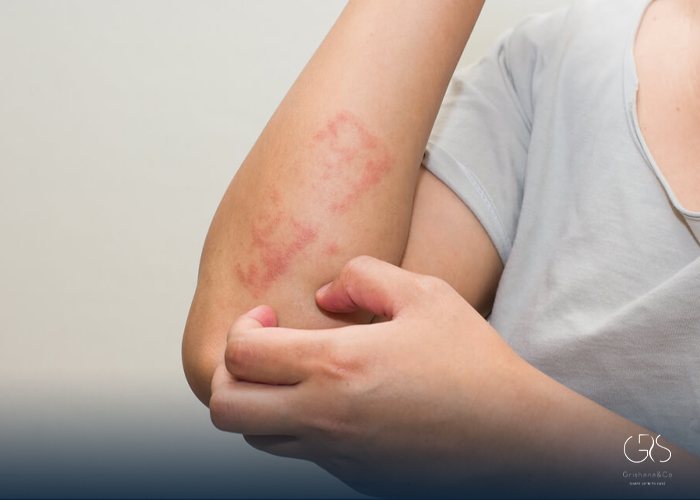
Treatment and Prevention
Immediate and appropriate treatment of anaphylactic shock is essential to prevent life-threatening complications. The administration of epinephrine is the primary treatment, as it helps to reverse the allergic response. Other interventions may include antihistamines, corticosteroids, and intravenous fluids.
Prevention is another crucial aspect of managing anaphylactic shock. Individuals with known allergies should avoid triggers and have an emergency action plan in place. Raising awareness in schools, workplaces, and public spaces is essential to ensure a supportive and safe environment for those at risk.
Diverse Perspectives
Understanding anaphylactic shock from diverse perspectives is essential for comprehensive management and support systems. It is crucial to consider the experiences and challenges faced by individuals with allergies, healthcare providers, and the community as a whole.
- Patient Perspectives: Empathizing with individuals who experience anaphylactic shock can foster a better understanding of the emotional and physical toll it takes. Acknowledging their challenges, educating others, and advocating for safe environments can make a significant difference.
- Healthcare Provider Perspectives: Healthcare providers play a critical role in diagnosing, treating, and educating patients about anaphylactic shock. Continuous professional training, development, and accessible resources are vital to ensure effective management.
- Community Perspectives: Raising awareness within the community promotes inclusivity and understanding. Initiatives such as allergy-friendly policies in schools, restaurants, and public spaces can contribute to a safer environment.
Conclusion
Anaphylactic shock is a severe, potentially life-threatening condition that requires swift recognition and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures is essential for individuals, healthcare providers, and society as a whole. By considering diverse perspectives and working together, we can create a safer and more inclusive environment for those at risk.
Sources
- American Academy of Allergy, Anaphylaxis
- WebMD, Anaphylaxis and Allergies
- Mayo Clinic, Anaphylaxis