Belly fat is a common concern for many individuals, as excess fat around the midsection is not only aesthetically undesirable but also a risk factor for various health conditions. However, recent research has shed light on the fact that not all belly fat is created equal. Understanding the different types of belly fat and how they can impact your health is crucial in taking steps towards a healthier lifestyle.
Types of Belly Fat
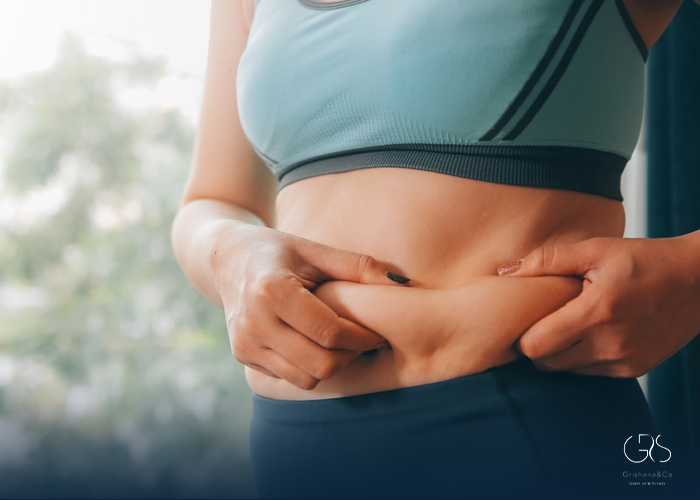
When it comes to belly fat, there are two main types: subcutaneous fat and visceral fat. Subcutaneous fat is the fat that lies just beneath the skin and is usually more visible. On the other hand, visceral fat is located deep within the abdomen, surrounding vital organs. While both types of fat can contribute to an increased waistline, visceral fat is particularly concerning as it has been linked to a higher risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
The Impact of Visceral Fat
Research has shown that excess visceral fat can release harmful substances into the bloodstream, leading to inflammation and insulin resistance. This can in turn contribute to the development of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, visceral fat has been associated with higher levels of “bad” cholesterol and lower levels of “good” cholesterol, further raising the risk of cardiovascular problems.
(If you want to learn about losing belly fat, please refer to this article)
Improving Your Belly Fat Health
While it may seem daunting to tackle belly fat, especially the visceral kind, there is hope. New research suggests that one key factor in reducing visceral fat and improving overall belly fat health is regular physical activity. Engaging in aerobic exercise, such as walking, running, or cycling, has been shown to be effective in burning calories and reducing visceral fat accumulation. Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or bodyweight exercises, can also help build muscle mass, which is important for boosting metabolism and burning fat.
(Read about how metabolism works.)
(I suggest that you read my article on calories while walking.)

Incorporating Healthy Habits
In addition to exercise, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support your efforts in reducing belly fat. Avoiding sugary beverages, processed foods high in trans fats, and excessive alcohol consumption can also aid in decreasing visceral fat levels. Moreover, managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can help prevent the release of stress hormones that can contribute to fat accumulation.
(Check out my article on exercise for depression)

Conclusion
Not all belly fat is the same, and understanding the difference between subcutaneous and visceral fat is crucial for your health. By incorporating regular physical activity, adopting a healthy diet, and managing stress, you can take proactive steps towards reducing visceral fat and improving your overall well-being.
Sources
- Harvard Health Publishing, Taking aim at belly fat
- WebMD, Your Best Ways to Beat Belly Fat
- Healthline, How to Get Rid of Visceral Fat