Body Mass Index (BMI) is often recognized as the go-to measure for determining an individual’s body composition and overall health. However, a growing number of researchers and health professionals are now leaning towards body fat percentage as a more accurate indicator of wellness. This article will delve into Body Fat Percentage vs. BMI, Why the Emphasis on Body Composition, What Is a ‘Healthy’ Body Fat Percentage, How Can You Find Your Body Fat Percentage, How Best to Manage Body Composition, and a conclusion.
Body Fat Percentage vs. BMI
In simple terms, BMI is a measure of an individual’s weight in relation to their height. While it is a useful tool for identifying obesity at the population level, it often fails to account for aspects such as muscle mass. This is where body fat percentage comes in, as it provides a more realistic representation of an individual’s body composition. Body fat percentage is a measure of fat mass in relation to lean body mass. While BMI cannot differentiate between fat and lean mass, body fat percentage can provide a more detailed picture of how an individual’s body is composed. For instance, an athlete with a low body fat percentage and high muscle mass may have a high BMI, indicating obesity despite having very little body fat.
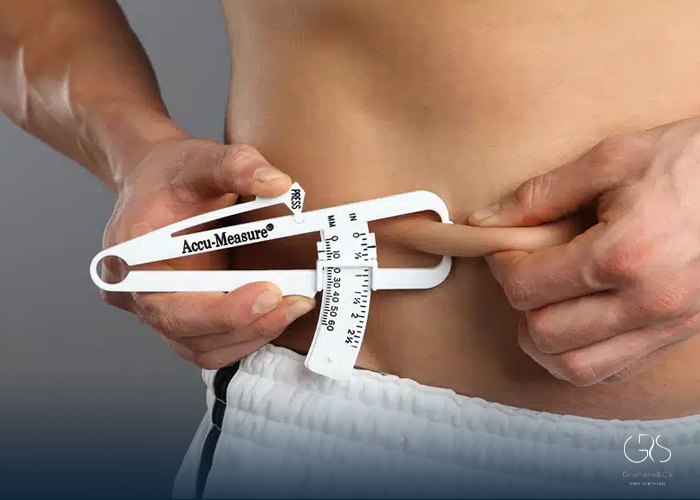

Why the Emphasis on Body Composition?
Body composition can be a better indicator of overall health than just using weight or BMI. Research has shown that body fat percentage is a better predictor of disease risk than BMI. For example, a study published by the International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders found that body fat percentage was more closely linked to diabetic complications than BMI. Body fat percentage is also associated with other health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers.
What Is a ‘Healthy’ Body Fat Percentage?
The definition of a healthy body fat percentage can vary depending on several factors such as gender, age, and activity level. However, generally, a healthy body fat percentage for females is somewhere between 20-25% and for males, between 10-15%.
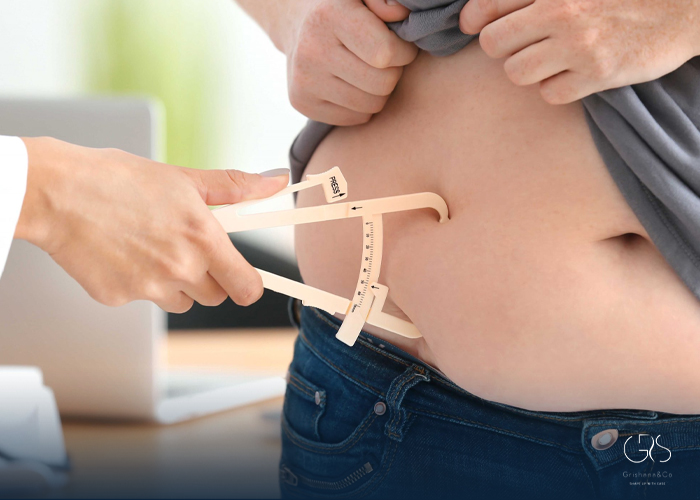
How Can You Find Your Body Fat Percentage?
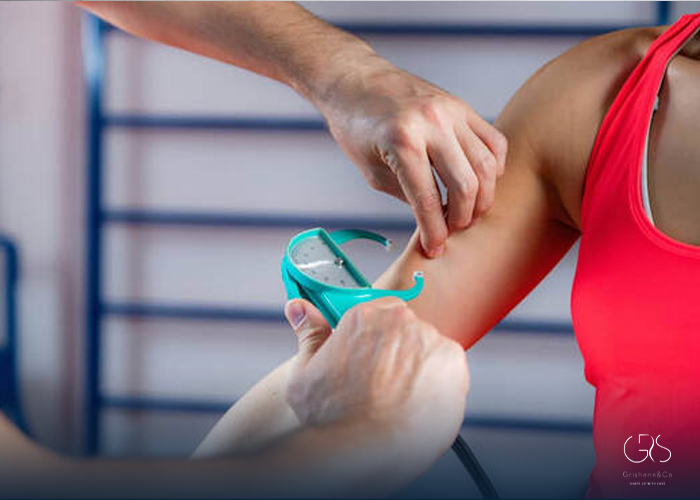
Various methods exist to determine your body fat percentage, including Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Skinfold thickness measurement, and Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis is a commonly used method that uses a small electrical current to measure body composition. Skinfold thickness measurement involves measuring the thickness of skinfolds at different sites on the body. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry uses low-level radiation to measure body composition. These methods can provide accurate results while being non-invasive and simple to carry out.
(Read more about Understanding Body Fat Percentage.)
How Best to Manage Body Composition
The key to managing body composition is a combination of healthy nutrition and regular exercise. Maintaining a modest calorie deficit is central, and consuming nutrient-dense foods such as whole-grains, lean protein, and leafy greens will help achieve this. Regular exercise should also be an integral part of a healthy lifestyle, engaging in high-intensity interval training or resistance training and workouts that build lean muscle mass, improving overall health, and reducing the risk of various health conditions.
Conclusion
It is important to consider both BMI and body fat percentage when assessing overall health and disease risk. Whereas BMI is a quick and easy tool to use for any population, body fat percentage, and body composition, in general, provides a more detailed picture of an individual’s overall health. Understanding and managing body composition through proper nutrition and exercise is a crucial part of achieving optimal health, preventing disease, and improving overall well-being.
According to the WHO, over 1.9 billion adults worldwide are overweight, while more than 650 million people are obese. These statistics present a serious issue that needs addressing, and both the use of BMI and body fat percentage play key roles in assessing, managing, and preventing these concerning health trends.
Sources
- Harvard Health Publishing, An inside look at body fat
- Mayo Clinic, BMI and waist circumference calculator
- World Health Organization , Obesity and overweight