Calcium deficiency symptoms are indicative of a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting healthy muscle function and nerve transmission. Despite its importance, many people around the world are not getting enough calcium in their diets, leading to potential health risks. In this article, we will explore the signs that indicate a calcium deficiency and offer insights into how to address this issue.
Understanding Calcium Deficiency
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the recommended daily intake of calcium for adults is around 1000-1300mg, varying by age and gender. Calcium is primarily found in dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fortified foods. However, many individuals, especially those following restrictive diets or with lactose intolerance, may struggle to meet their daily calcium requirements.
When the body does not receive an adequate amount of calcium, it starts to draw from existing calcium stores in the bones, leading to weakened bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis over time. Recognizing the signs of calcium deficiency is crucial to address the issue before it escalates into more severe health conditions.
Signs of Calcium Deficiency
1.Frequent Bone Fractures: Individuals who do not consume enough calcium may experience more frequent bone fractures due to weakened bone density.
2.Muscle Cramps and Spasms: Calcium plays a key role in muscle contraction and relaxation. A deficiency can lead to muscle cramps or spasms, especially during physical activity.
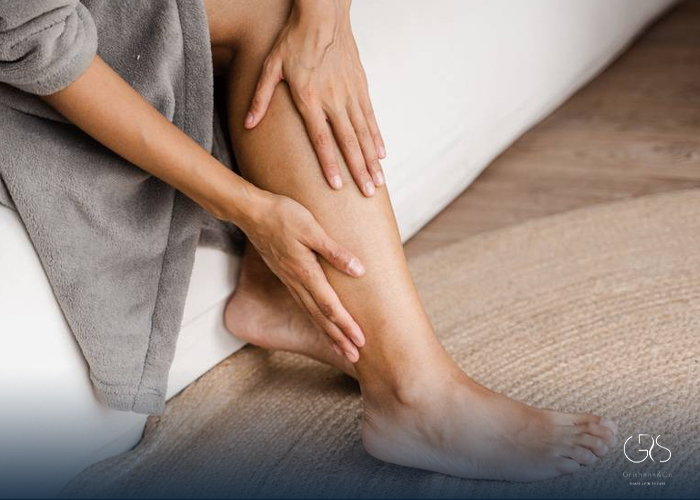

3.Numbness and Tingling Sensations: Inadequate calcium intake can affect nerve function, leading to numbness or tingling sensations in the hands, feet, or face.
4.Fatigue and Weakness: Calcium is essential for energy production in the body. A deficiency can cause fatigue, weakness, and a general sense of lethargy.

5.Dental Problems: Insufficient calcium intake can affect dental health, leading to weakened tooth enamel, cavities, and an increased risk of periodontal disease.
6.Brittle Nails: Brittle, easily breakable nails can be a sign of calcium deficiency, as calcium is essential for nail health and strength.
7.Heightened PMS Symptoms: Some studies suggest that low calcium levels may exacerbate premenstrual symptoms in women, including mood swings, bloating, and cramps.
Addressing Calcium Deficiency
If you suspect you are not getting enough calcium in your diet, there are several steps you can take to boost your intake:
1.Diversify Your Diet: Include calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified cereals in your meals to ensure an adequate intake of this essential mineral.
2.Consider Supplements: If you are unable to meet your calcium needs through diet alone, consult with a healthcare professional to determine if calcium supplements are needed.
3.Sunlight Exposure: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption. Ensure you get enough sunlight exposure or consider taking a Vitamin D supplement to support calcium absorption.
(If you’re interested in reading about foods high in calcium)

4.Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of caffeine and alcohol can interfere with calcium absorption. Limiting these substances may help improve your calcium levels.
5.Regular Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, running, or strength training can help maintain bone density and support overall bone health.

Diverse Perspectives on Calcium Deficiency
It is essential to acknowledge that access to diverse sources of calcium can vary based on cultural, dietary, and economic factors. In some regions, dairy products are a primary source of calcium, while in others, plant-based alternatives may be more commonly consumed.
For individuals who follow vegetarian or vegan diets, obtaining enough calcium from plant-based sources like leafy greens, fortified non-dairy milk, and tofu is crucial. Additionally, lactose intolerance or dairy allergies may necessitate alternative calcium-rich foods or supplements to meet daily requirements.
Furthermore, socioeconomic factors can impact an individual’s ability to access nutrient-dense foods rich in calcium. Addressing disparities in food availability and affordability is essential to ensure everyone has the opportunity to maintain adequate calcium levels for optimal health.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of calcium deficiency symptoms and taking proactive steps to address inadequate intake is crucial for overall health and well-being. By incorporating a variety of calcium-rich foods, considering supplements if needed, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can support their bone health and minimize the risk of calcium-related complications. Remember, if you experience persistent symptoms of calcium deficiency or have concerns about your calcium intake, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
Sources
- National Institutes of Health, Calcium
- Mayo Clinic, Calcium and calcium supplements: Achieving the right balance
- Harvard Health Publishing, Calcium