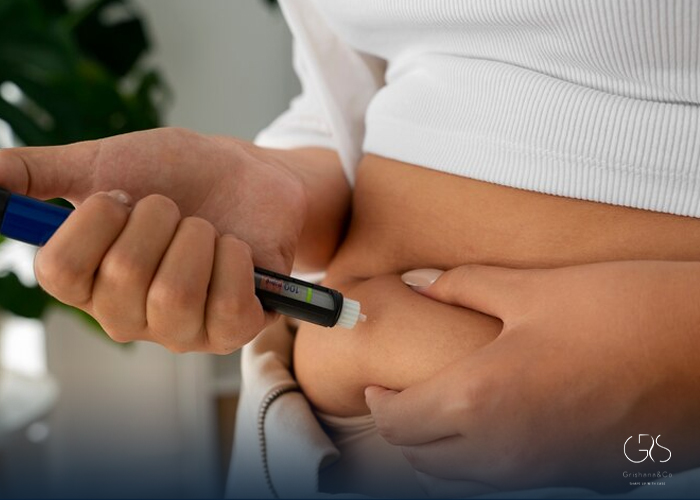
Diabetes Risk Factors, a complex and chronic condition, affects millions globally and demands significant attention for its severe health implications. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of people with diabetes has escalated from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014, underscoring its status as a paramount health challenge of the contemporary era (WHO).
Types of Diabetes
There are mainly two primary types of diabetes – Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes commonly emerges in children and young adults and is characterized by the body’s failure to produce insulin. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes , the more prevalent form, typically develops in adults and entails the body’s ineffective use of insulin, which leads to insulin resistance.
(I suggest reading about type 2 diabetes with Mounjaro.)
Risk Factors for Diabetes
- Family History: Genetic predisposition plays a substantial role in diabetes development. Individuals with a family history of diabetes face an increased risk of developing the condition.
- Lifestyle Choices: Factors such as poor dietary habits, physical inactivity, and obesity contribute significantly to the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
- Age and Ethnicity: Individuals aged 45 and above, as well as those from specific ethnicities such as African American, Hispanic, Native American, or Asian American, are at a heightened risk of diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Women who have experienced gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at an elevated risk of developing Type 2 diabetes in the future.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
Key signs and symptoms of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: Experiencing excessive thirst and needing to urinate more frequently are common indicators of diabetes.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Inexplicable weight loss despite normal eating habits can be a sign of diabetes.
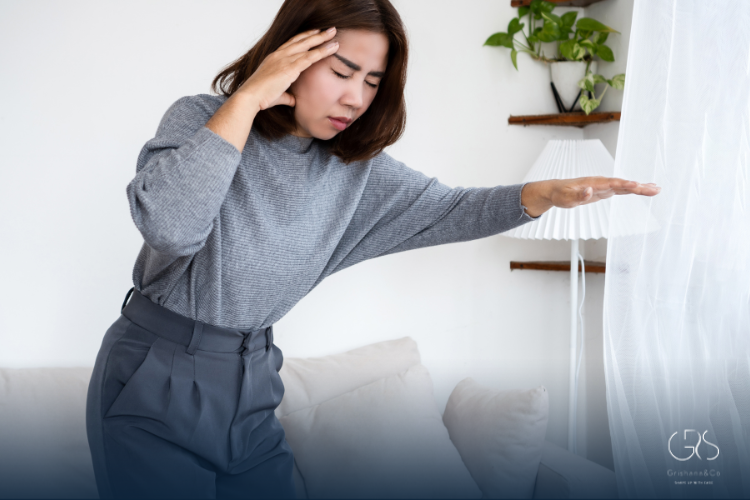
- Fatigue and Irritability: Persistent fatigue, irritability, and even mood swings can signify diabetes.
- Blurred Vision: Diabetes can lead to changes in vision, causing blurriness or difficulty focusing.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Long-lasting sores or wounds that heal slowly are potential symptoms of diabetes.
Preventive Measures
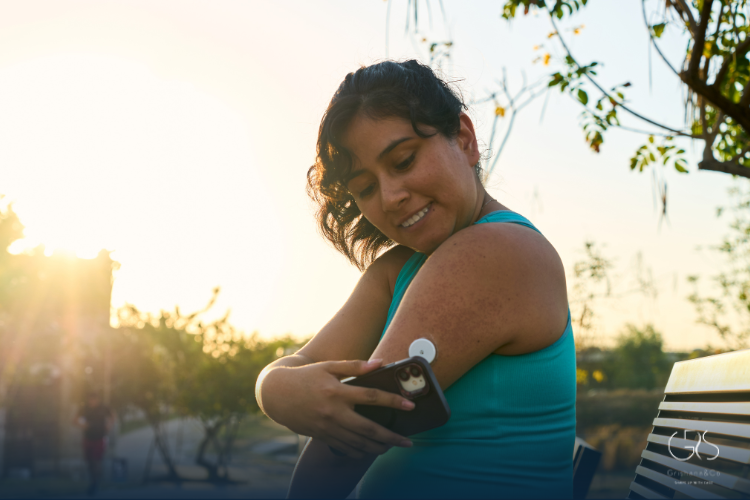
Preventive measures for diabetes include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, monitoring blood sugar levels, and avoiding tobacco use.
Engaging in proactive lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes. Key preventive measures include:
1.Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Shedding excess weight and embracing a balanced diet coupled with regular physical activity can help prevent the onset of diabetes.

2.Adopting a Healthy Diet: Prioritizing a varied diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting sugar, processed foods, and saturated fats.
3.Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate-intensity activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for a minimum of 30 minutes daily can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
(I recommend reading my article about the health benefits of swimming)
(We recommend that you read this article on walking speed and type 2 diabetes.)

4.Regular Health Check-ups: Routine screenings and check-ups are crucial for monitoring blood sugar levels and detecting early signs of diabetes, enabling prompt intervention and management.
While these preventive measures hold promise in minimizing the risk of diabetes, it is imperative for individuals to seek personalized guidance from healthcare professionals for tailored advice and support.
Diverse Perspectives on Diabetes Risk and Prevention
In addition to the conventional risk factors and preventive strategies, it is vital to acknowledge the diverse and intersectional nature of health disparities. Various demographic, social, and economic factors play roles in an individual’s susceptibility to diabetes and their capacity to access prevention resources and healthcare services.
Socioeconomic Factors:
Individuals from marginalized socioeconomic backgrounds often face barriers to accessing nutritious food, engaging in physical activity, and obtaining quality healthcare. This can lead to increased susceptibility to diabetes and its complications.
Cultural and Ethnic Influences:
Cultural and ethnic diversity contributes significantly to variations in diabetes prevalence, risk factors, and preventive approaches. Acknowledging cultural dietary practices, lifestyle norms, and health beliefs is critical in tailoring prevention strategies to specific communities.
Gender Disparities:
Research has shown that gender disparities exist in the prevalence of diabetes, with women facing unique risk factors such as gestational diabetes. Understanding and addressing these gender-specific risk factors is essential for comprehensive diabetes prevention efforts.
Geographical Considerations:
Geographical location can impact diabetes risk, with individuals in certain regions facing environmental and infrastructural challenges that hinder healthy lifestyle choices and access to healthcare.
Conclusion
Comprehensive understanding of the risk factors, signs, and preventive measures for diabetes is paramount in addressing and mitigating this prevalent health condition. By incorporating diverse perspectives, promoting equitable access to healthcare, and tailoring preventive efforts to specific communities, it is possible to make tangible progress in reducing the impact of diabetes on global health.
Sources
- World Health Organization, Diabetes
- American Diabetes Association, Diabetes