When it comes to incorporating fruits into our diet, one common dilemma that arises is whether to choose fresh or frozen fruit. Both options have their own set of benefits and drawbacks, influencing factors such as nutrition, taste, cost, and shelf-life. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of fresh and frozen fruit consumption, compare their nutritional value, explore the advantages and disadvantages of each, and provide tips for maximizing the benefits of both options.
Nutrition Comparison
Fresh Fruit:
Fresh fruits are often perceived as the epitome of health due to their natural form and vibrant colors. They are rich sources of essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. The nutritional content in fresh fruit is at its peak when consumed immediately after harvest, as certain vitamins like vitamin C can degrade over time.
(Read more about benefits of vitamin C)

Frozen Fruit:
On the other hand, frozen fruits are picked at their peak ripeness and flash-frozen to preserve their nutrients. Studies have shown that in some cases, the vitamin and mineral content of frozen fruits may be higher than that of fresh fruits stored for an extended period. This is because freezing helps to inhibit the degradation of certain nutrients, making them available for consumption even during off-seasons.
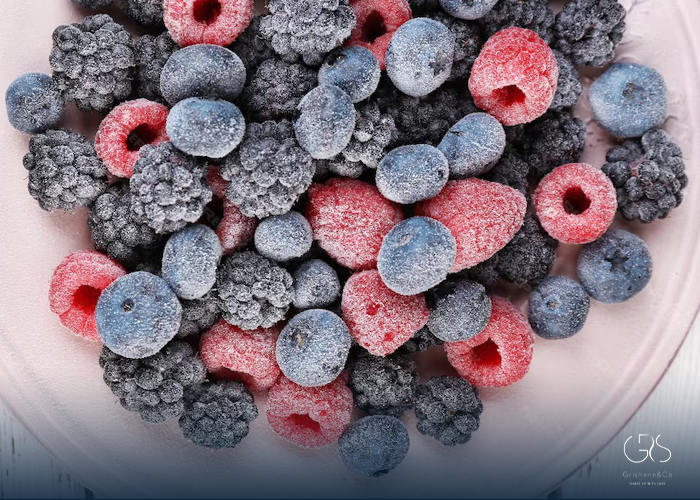

Benefits of Eating Fresh and Frozen Fruit
Benefits of Fresh Fruit:
- Higher water content helps in hydration.
- Typically better taste and texture compared to some frozen options.
- Immediate availability of nutrients if consumed soon after harvest.
Benefits of Frozen Fruit:
- Longer shelf-life makes it convenient for meal planning.
- Available year-round, ensuring a constant supply of nutritious fruits.
- Retains nutrient content due to the preservation process of flash-freezing.
Downsides of Fresh vs. Frozen Fruit
Fresh Fruit:
- Can be expensive, especially when out of season.
- Short shelf-life, leading to possible food waste if not consumed promptly.
- Nutrient degradation over time if not consumed quickly.
Frozen Fruit:
- Some varieties may lose their texture and taste after freezing and thawing.
- Limited availability of exotic and seasonal fruits in frozen form.
- Some brands may add sugar or preservatives, impacting overall health benefits.
Taste and Texture
Taste and texture play a significant role in determining consumer preference for fresh or frozen fruit. While fresh fruit is known for its juiciness and crispness, frozen fruit can be softer and slightly mushy after thawing. However, for uses like smoothies, baking, and sauces, the texture of frozen fruit can actually be advantageous, as it blends well and imparts a thicker consistency to dishes.
Cost and Shelf-Life
In terms of cost, fresh fruit can often be more expensive, especially if purchasing fruits out of season. On the other hand, frozen fruit offers a more budget-friendly option, allowing consumers to access a variety of fruits throughout the year without breaking the bank.
Shelf-life is another crucial factor to consider. Fresh fruit typically has a shorter shelf-life, requiring more frequent grocery trips to ensure freshness. Frozen fruit, on the other hand, can be stored for longer periods without the risk of spoilage, making it a more convenient option for those with busy schedules or limited access to fresh produce.
Frozen Fruit vs. Canned Fruit
While frozen fruit is often perceived as a healthier alternative to canned fruit, it is important to note that the sugar content in canned fruit can vary based on whether it is packed in syrup, juice, or water. Frozen fruit, when minimally processed and free from added sugars, retains much of its natural nutrient content, making it a better choice for those looking to optimize their health.
Tips for Consuming Frozen Fruit
To make the most of frozen fruit in your diet, consider the following tips:
- Use frozen fruit in smoothies, yogurt bowls, and baking for added flavor and nutrition.
- Thaw frozen fruit in the refrigerator to preserve texture and taste.
- Experiment with different combinations of frozen fruits to discover new flavor profiles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both fresh and frozen fruits have their own unique set of advantages and disadvantages. While fresh fruit is prized for its taste and immediate availability of nutrients, frozen fruit offers convenience, cost-effectiveness and a longer shelf-life. Ultimately, the best choice between fresh and frozen fruit depends on individual preferences, dietary needs, and lifestyle factors. By incorporating a mix of fresh and frozen fruits into your diet, you can enjoy a diverse range of flavors and reap the health benefits that each option provides.
Sources
- Healthline, Fresh vs Frozen Fruit and Vegetables — Which Are Healthier?
- Harvard Health, Reconsider frozen fruits and vegetables
- USDA, Frozen Mixed Vegetables Grades and Standards