Heartburn, characterized by a burning sensation in the chest, is a common condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. While occasional heartburn is often manageable, chronic heartburn can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore the symptoms of heartburn, identify potential causes, and discuss remedies to alleviate its discomfort. We will also consider diverse perspectives and provide relevant statistics to offer a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
Symptoms of Heartburn
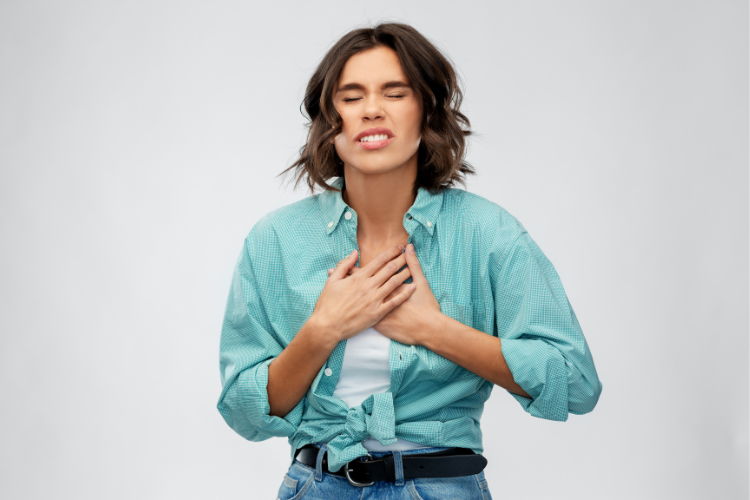
Heartburn typically presents as a burning sensation in the chest, usually after eating or while lying down. However, the symptoms may vary in intensity and duration. As per data from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), around 60 million Americans experience heartburn at least once a month. In addition to the burning feeling, individuals may experience regurgitation, sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and even chronic cough. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms to differentiate heartburn from other underlying conditions like GERD or peptic ulcers.
Causes of Heartburn
Understanding the causes of heartburn is key to managing the symptoms effectively. Several factors contribute to the occurrence of heartburn, including diet, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions. Certain foods like citrus fruits, tomatoes, fatty or spicy foods, and beverages like coffee or alcohol are known triggers. Obesity, smoking, and stress have also been associated with an increased risk of heartburn. Further, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic form of acid reflux that often leads to severe heartburn. Furthermore, hormonal changes during pregnancy can also cause heartburn.
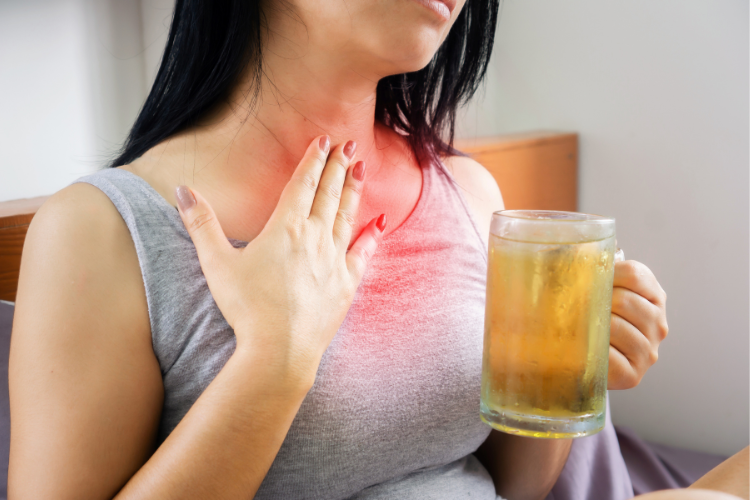

Risks and Complications of Untreated Heartburn
Although heartburn is generally considered harmless, frequent episodes can pose long-term risks if left untreated. Chronic heartburn can lead to complications like esophageal strictures, where the esophagus narrows, making swallowing difficult. In rare cases, it may even lead to Barrett’s esophagus, a precancerous condition. These potential complications highlight the importance of managing heartburn symptoms promptly and effectively.
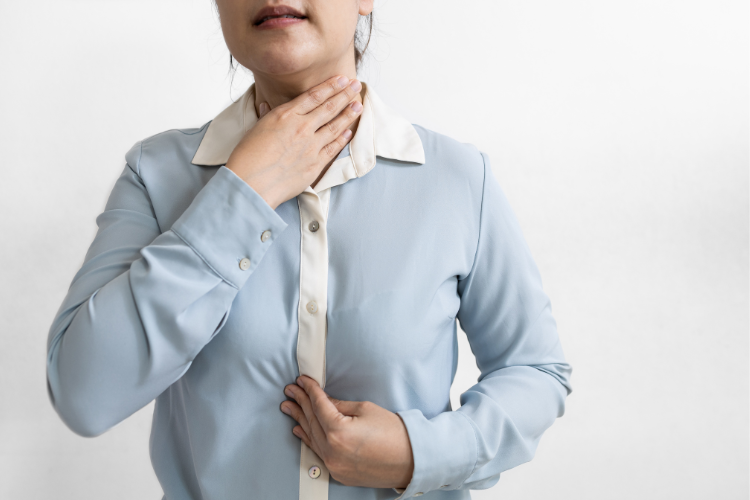

Remedies for Heartburn
Thankfully, several remedies exist for heartburn relief. Over-the-counter antacids provide temporary relief from symptoms by neutralizing stomach acid. Additionally, lifestyle modifications can help prevent heartburn. Simple measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods and eating smaller meals can significantly reduce the occurrence of heartburn. For individuals with chronic heartburn, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 blockers can be prescribed to reduce acid production. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication.
Diverse Perspectives on Heartburn Management
While exploring diverse perspectives, it is essential to acknowledge alternative approaches to managing heartburn symptoms. Some individuals may opt for natural remedies like herbal teas, ginger, or slippery elm, known for their soothing effects on the digestive system. However, it is crucial to note that evidence supporting the efficacy of these remedies is limited and varies from person to person. Therefore, consultation with a healthcare professional remains essential.
Conclusion
Heartburn is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms of heartburn and understanding its causes are crucial steps towards managing and preventing its occurrence. Various remedies, including medication, lifestyle modifications, and natural alternatives, offer relief from heartburn symptoms. By adopting a comprehensive approach and seeking professional advice when needed, individuals can alleviate the discomfort caused by heartburn and enjoy a better quality of life.
Sources
- American College of Gastroenterology, Understanding Heartburn and Reflux Disease. Retrieved
- Mayo Clinic, Heartburn. Retrieved
- Harvard Health Publishing, Foods that fight heartburn. Retrieved
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Symptoms & Causes of GER & GERD
- American Cancer Society, Barrett Esophagus. Retrieved
- Cleveland Clinic, Medications for GERD Treatment
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, Ginger. Retrieved