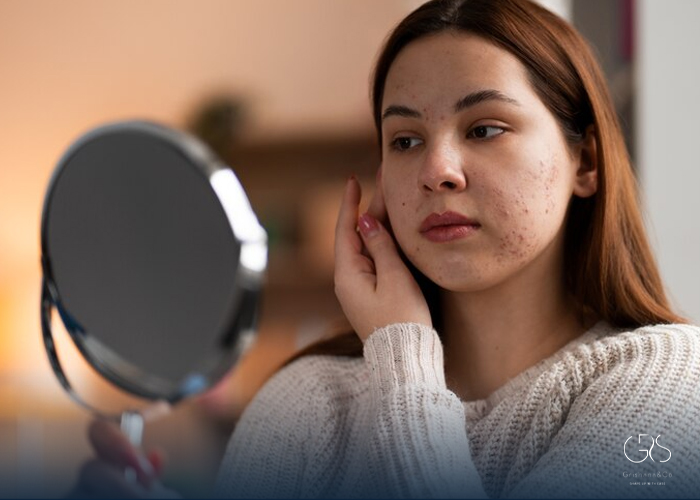
In recent years, the beauty and skincare industry has witnessed the rise of various ingredients, each claiming exceptional benefits. Among these compounds, Mandelic acid has gained significant attention for its potential in treating various skin conditions and promoting overall skin health. This article aims to provide a comprehensive review of Mandelic acid, exploring its origins, chemical properties, uses, and potential benefits.
What is Mandelic Acid?
Mandelic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) derived from bitter almonds. Initially discovered in 1832 by a German chemist Ferdinand von Mandel, this compound has long been recognized for its antibacterial and exfoliating properties. Its unique molecular structure differentiates it from other AHAs, such as glycolic and lactic acids, giving it distinct advantages.
Chemical Properties and Mechanism of Action
Mandelic acid has a larger molecular structure, providing the potential for slower and controlled penetration into the skin. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for individuals with sensitive skin or those prone to irritations caused by more aggressive exfoliation methods. Due to its larger size, Mandelic acid molecules effectively target the skin’s surface layer, aiding in exfoliation, and unclogging pores without causing excessive irritation.
Current research suggests that Mandelic acid primarily works by accelerating the skin’s natural cell turnover rate, stimulating the creation of collagen and elastin, promoting hydration, and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Additionally, it exhibits antimicrobial properties that make it effective against acne-causing bacteria, making it a potential solution for individuals struggling with acne-prone skin.
Uses and Benefits
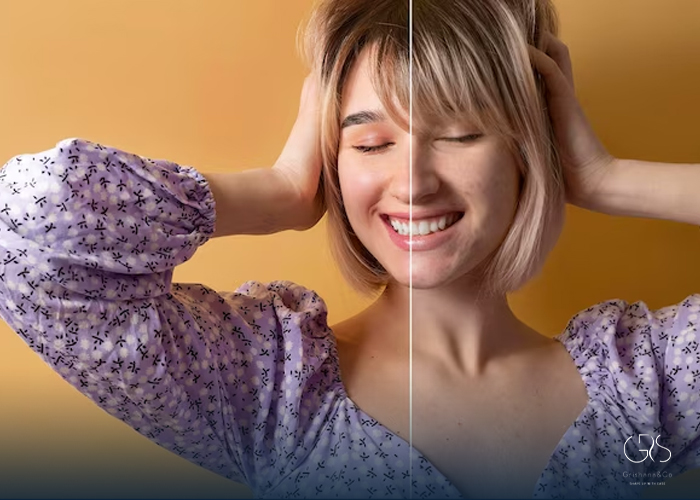
1.Anti-aging Properties: Studies have shown that Mandelic acid helps to improve the appearance of aging skin by reducing the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and hyperpigmentation . It is also known to enhance the skin’s overall texture, resulting in a smoother and more youthful complexion.
2.Treatment for Acne: The antibacterial properties of Mandelic acid make it effective in combating acne. Its gentle exfoliating action helps to unclog pores, reduces sebum production, and prevents the formation of new acne lesions . Furthermore, this AHA has been found to be less irritating than other AHAs, making it more suitable for individuals with sensitive or acne-prone skin.
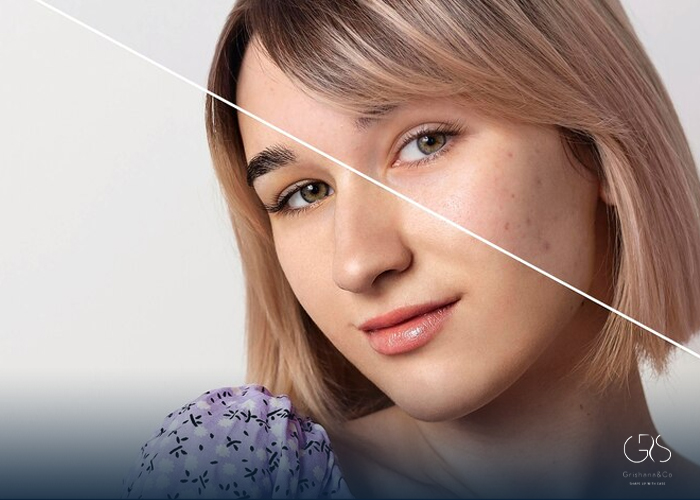
3.Skin Brightening and Hyperpigmentation: Mandelic acid is recognized for its ability to address skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation. It inhibits the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for dark spots, resulting in a more even skin tone .
Diverse Perspectives
While Mandelic acid offers numerous benefits, it is crucial to consider diverse perspectives on its usage. Some critics argue that the research surrounding Mandelic acid is still relatively limited compared to other AHAs. They assert that further studies are necessary to fully comprehend its long-term effects, potential adverse reactions, and compatibility with different skin types.
Others highlight the importance of consulting with skincare professionals before incorporating Mandelic acid into a beauty regimen. They emphasize the need to assess individual skin concerns, type, and existing conditions alongside the ingredient to ensure optimal results and minimal risk.
Conclusion
Mandelic acid, an alpha hydroxy acid derived from bitter almonds, has emerged as a promising ingredient in the skincare industry. With its unique properties, Mandelic acid offers potential benefits for aging skin, acne treatment, and hyperpigmentation issues. However, it is imperative to approach its usage with care, considering diverse perspectives, and seeking professional advice when incorporating it into skincare routines.
Sources
- PubMed Central, Mandelic Acid: A Promising Alpha Hydroxy Acid for Skincare
- Wiley Online Library, The Efficacy and Safety of Mandelic Acid in Acne Treatment
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, Depigmenting Effect of Mandelic Acid