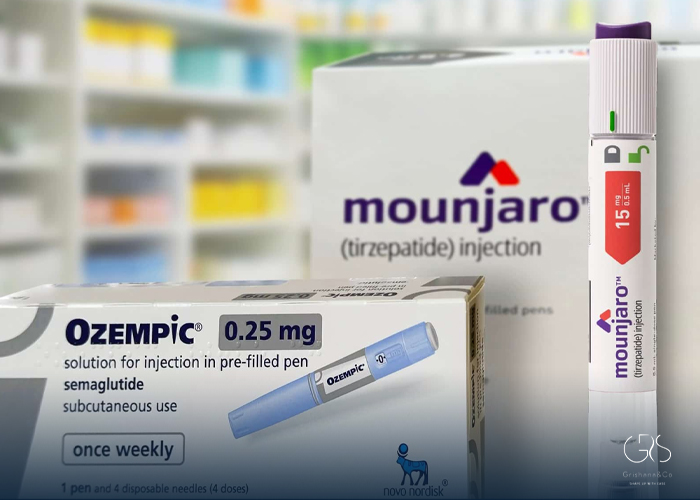
Mounjaro and Ozempic are both injectable medications used to treat type 2 diabetes. While they share some similarities, there are also key differences between the two drugs in terms of how they work, their biological mechanisms, effectiveness, and potential benefits. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals living with diabetes and their healthcare providers to make informed treatment decisions.
What Do Mounjaro and Ozempic Do?
Mounjaro (semaglutide) and Ozempic (semaglutide) both belong to the class of medications known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. They work by mimicking the action of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in the body. This helps to regulate blood sugar levels, suppress appetite, and reduce the release of glucose from the liver.
How Mounjaro Works
Mounjaro , with the active ingredient semaglutide, works by stimulating the release of insulin and inhibiting the release of glucagon from the pancreas. This mechanism helps to lower blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes .
How Ozempic Works
Ozempic , also containing semaglutide, functions in a similar way to Mounjaro by increasing insulin production and decreasing glucagon release. This results in improved blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes.

Similarities Between Mounjaro and Ozempic
Both Mounjaro and Ozempic share the same active ingredient, semaglutide. They are both indicated as adjuncts to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Differences Between Mounjaro and Ozempic
The main difference lies in their approved dosing regimens. Mounjaro is available in various dosages ranging from 0.25mg to 2.0mg, while Ozempic is typically available in a fixed dosage of 0.5mg and 1.0mg.
According to a recent study, the active ingredient tirzepatide in Mounjaro may demonstrate superior efficacy in promoting weight loss compared to semaglutide, the active compound in Ozempic.
How They Work Biologically
Biologically, both medications act on the GLP-1 receptor to regulate blood sugar levels, but their specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties may vary.
Effectiveness
Both Mounjaro and Ozempic have shown effectiveness in reducing HbA1c levels and aiding in weight management in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, individual responses to each medication may vary, and efficacy should be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
Heart Health Benefits
Studies have suggested that both medications may have potential cardiovascular benefits, including reducing the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes (source).
Dose and Administration
Mounjaro is administered once weekly, while Ozempic is typically given as a once-weekly injection. Proper administration technique, storage, and titration should be followed as per the prescribing information for each medication.
Can You Switch From Ozempic to Mounjaro or Vice Versa?
Switching between these medications should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Factors such as dosing, current glycemic control, and individual patient needs should be taken into consideration when transitioning from one medication to the other.
Conclusion
While Mounjaro and Ozempic share similarities in their mechanism of action and intended use, there are important differences in their dosing, additional indications, and specific pharmacokinetic properties. Patients and healthcare providers should work together to determine the most suitable treatment regimen based on individual needs and preferences.
Sources
- The New England Journal of Medicine , Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes
- American Diabetes Association, Oral & Injectable Medications for Type 2 Diabetes