Mounjaro, an FDA-approved medication developed by Eli Lilly for managing type-2 diabetes, utilizes a novel mechanism to improve clinical outcomes. Its active ingredient, tirzepatide, functions as a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, enhancing its efficacy beyond traditional GLP-1 agonists. This article aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of how Mounjaro works, along with relevant statistics and diverse perspectives.
The Mechanism of Action:
Tirzepatide, the active ingredient in Mounjaro, acts by mimicking the effects of incretin hormones—namely, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). After consuming a meal, the body naturally releases incretin, which signals satiety and triggers a reduction in food intake. Tirzepatide complements the binding ability of GLP-1 with the greater potency of GIP agonists, effectively enhancing the feeling of fullness and reducing cravings. Furthermore, it helps in mitigating insulin resistance, contributing to a reduced desire for sugary or unhealthy foods.
(Learn more about the Mounjaro mechanism.)
Clinical Efficacy and Weight Loss:
Clinical studies have shown promising results regarding the weight loss properties of Mounjaro. According to the prescribing information provided by Eli Lilly, individuals with type 2 diabetes experienced an average weight loss of approximately 17 pounds over a 40-week period with the inclusion of diet and exercise. Additionally, another clinical study demonstrated a weight loss of up to 23% with once-weekly 15mg Mounjaro injections. These statistics underscore the potential of Mounjaro in aiding weight management, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes who struggle with obesity .
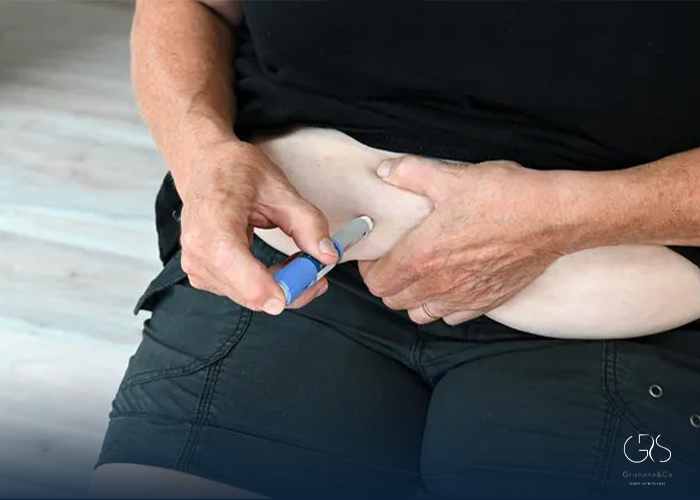
Administration and Frequency:
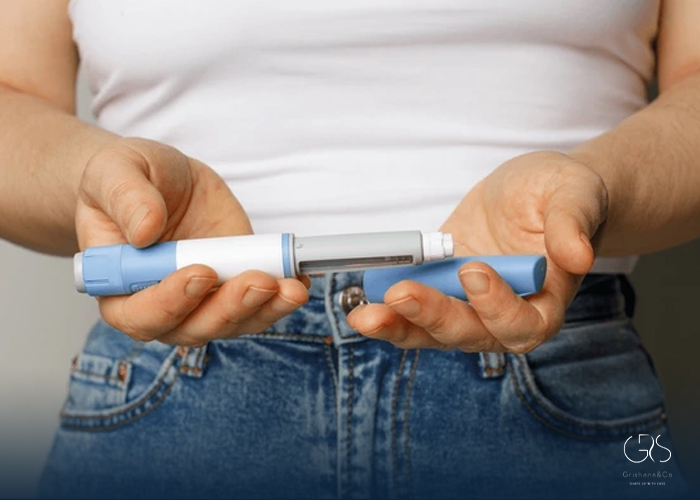
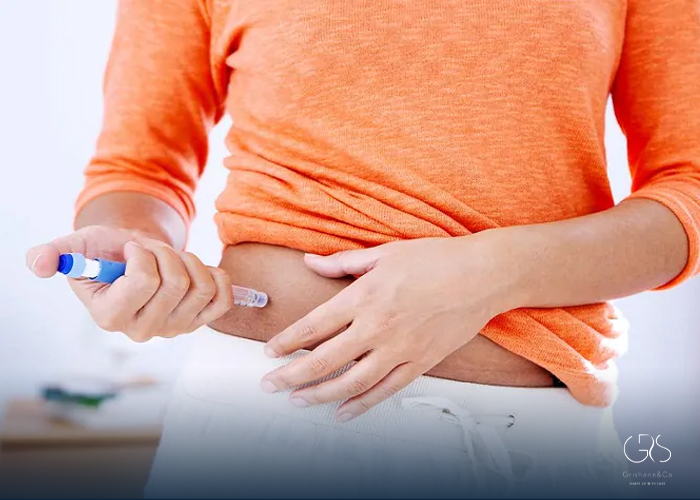
Mounjaro is administered as a once-weekly injection, conveniently packaged in a pen with a needle. The simplicity of this delivery method, coupled with the need for only weekly dosage, enhances the medication’s ease of use for patients. Additionally, the prepackaged pens reduce the need for extensive preparation, making the administration process relatively painless and user-friendly.
Off-Label Use for Weight Loss:
While Mounjaro is not FDA-approved specifically for weight loss, healthcare professionals have the discretion to prescribe medications off-label if they believe it to be an appropriate course of treatment for a particular patient. This provides a nuanced perspective on the potential applications of Mounjaro beyond its approved indication, acknowledging the importance of individualized treatment plans.
Consideration of Side Effects and Black-Box Warning:
It is essential to consider potential side effects and safety warnings associated with Mounjaro. The most common side effects reported include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, and stomach pain, among others. While these are generally considered normal and non-serious, it is crucial to seek guidance from healthcare professionals if any concerns arise. Additionally, Mounjaro carries a black-box warning regarding the risk of thyroid C-cell tumors, specifically contraindicating its use in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) (source: Mounjaro Prescribing Information).
Diverse Perspectives:
Considering diverse perspectives, it is evident that Mounjaro presents a potential opportunity for individuals with type 2 diabetes to manage their condition effectively while also addressing weight-related concerns. By integrating scientific evidence, clinical statistics, and safety considerations, a comprehensive understanding of Mounjaro’s mechanism of action and its implications can be achieved.
Conclusion:
Mounjaro’s mechanism of action, coupled with pertinent statistics and diverse perspectives, underscores its potential as a valuable tool in managing type 2 diabetes and associated weight concerns.
Sources
- Eli Lilly, MOUNJARO- tirzepatide injection, solution
- American Diabetes Association, Oral & Injectable Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
- WebMD, Mounjaro (tirzepatide) - Uses, Side Effects, and More