Obesity is a global health concern affecting millions of individuals worldwide. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of safe and effective ways to manage obesity. Harnessing statistics and diverse perspectives, we will explore seven proven methods to help individuals achieve sustainable weight loss and enhance overall well-being.
Balanced Diet and Portion Control:
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for managing obesity. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains ensures a well-rounded intake of essential vitamins and minerals. Additionally, portion control plays a vital role in managing weight. Moderating portion sizes helps avoid overeating and promotes a healthier calorie balance.

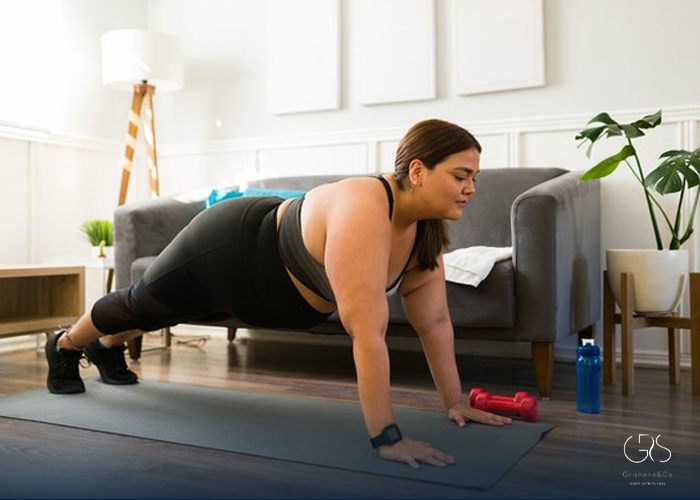
Regular Physical Activity:
An active lifestyle plays a key role in managing obesity. Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps burn calories but also improves cardiovascular health, boosts metabolism, and enhances overall fitness. Activities like walking, swimming, cycling, and strength training can be incorporated into daily routines to promote weight loss and long-term weight management.
(Interested in learning about the health benefits of swimming? Check out this article for valuable information.)

Behavior Modification:
Changing unhealthy behaviors and adopting positive habits is essential for managing obesity. Behavior modification techniques, such as keeping a food diary, setting realistic goals, and practicing mindful eating, can help individuals make conscious decisions about food choices and portion sizes. By identifying triggers and developing coping strategies, individuals can break harmful eating patterns.
Psychological Support:
Obesity management often requires addressing psychological factors that contribute to overeating or weight gain. Seeking professional psychological support, such as counseling or group therapy, can provide individuals with the tools and strategies needed to overcome emotional challenges associated with obesity. Addressing mental health and emotional well-being is crucial for achieving long-term success.
Medication and Medical Interventions:
In some cases, medication or medical interventions may be necessary to manage obesity. Under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals, prescription medications or weight loss interventions, such as bariatric surgery, may be considered. These approaches are typically recommended for individuals with severe obesity or obesity-related health complications.

Adequate Sleep:
Getting enough quality sleep is often overlooked in obesity management. Sleep deprivation can disrupt appetite-regulating hormones, leading to increased hunger and a higher risk of weight gain. Prioritizing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a conducive sleep environment can support healthy weight management and overall well-being.
Long-Term Support and Maintenance:
Sustainable weight management requires long-term commitment and support. Engaging in support groups, working with registered dietitians, or joining weight loss maintenance programs can provide ongoing guidance, motivation, and accountability. Regular check-ins and continuous education help individuals sustain healthy lifestyles and prevent weight regain.
Conclusion:
Managing obesity encompasses a multifaceted approach, addressing dietary, physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. By implementing the seven safe and effective methods mentioned above, individuals can take charge of their health, achieve weight management goals, and improve overall well-being.
Sources
- World Health Organization, Obesity
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Obesity - What You Can Do
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Obesity Prevention Programs