Oral cancer, a relatively common type of cancer, poses a serious health threat to millions of people around the world. The condition is often linked to lifestyle factors, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet. Recently, new research has suggested that there may be a connection between the consumption of soda and an increased risk of developing oral cancer. While the link between soda and oral cancer is still under investigation, the findings of these studies have raised concerns and sparked debate among health professionals and the public.
Understanding Oral Cancer
Before delving into the potential link with soda consumption, it is important to understand oral cancer itself. Oral cancer refers to cancer that develops in the mouth, including the lips, tongue, gums, and the roof and floor of the mouth. According to the American Cancer Society, an estimated 54,000 new cases of oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021, making it a significant public health concern. The condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Soda Consumption and Health Concerns
Soda, often marketed and consumed as a popular carbonated beverage, has long been the subject of health-related debates. Studies have linked excessive soda consumption to various health concerns, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and dental issues. These health risks are primarily attributed to the high sugar content and acidic nature of most sodas.
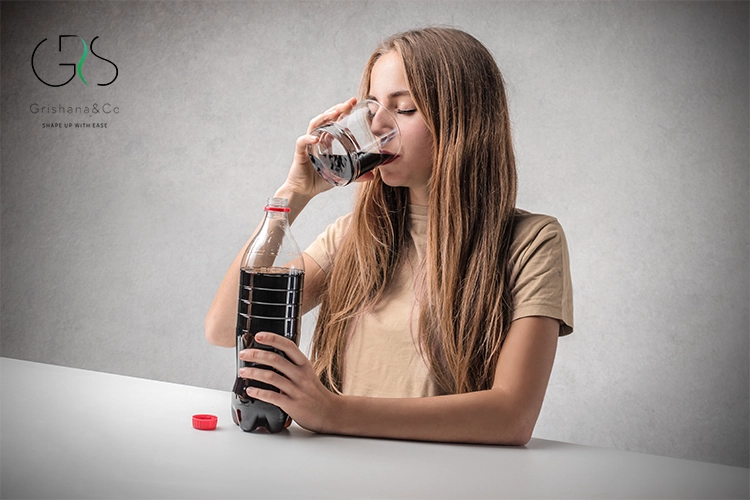

Oral cancer and soda: the new research raising concerns
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2019 caught the attention of the medical community by suggesting a potential link between soda consumption and the risk of developing oral cancer. The study, conducted by a team of researchers from multiple institutions, analyzed data from a large cohort of individuals over several years. The findings indicated that individuals who consumed higher amounts of sugary soda on a daily basis had a notably increased risk of developing certain types of oral cancer, even after accounting for other known risk factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption.
(Read about alcohol consumption limits.)
This ignited a new wave of interest in exploring the relationship between soda and oral cancer. Subsequent studies have attempted to replicate these findings and provide further insights into the potential mechanisms underlying this association. While not all studies have yielded consistent results, the idea that soda consumption might contribute to the development of oral cancer has gained traction in the scientific community.
Diverse Perspectives
The potential link between soda consumption and oral cancer has generated a spectrum of perspectives within the medical and public health domain. Some experts argue that the evidence linking soda to oral cancer is inconclusive and that further research is needed to establish a definitive association. They stress the importance of considering multiple factors, such as genetic predisposition, overall diet, and lifestyle habits, before drawing conclusions about the specific role of soda in the development of oral cancer.
Conversely, proponents of the link highlight the need for public health interventions to reduce soda consumption, especially among vulnerable populations. They call for greater awareness of the potential risks associated with excessive soda intake and advocate for policies aimed at curbing the consumption of sugary beverages, including soda, to mitigate the burden of oral cancer and other related health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the potential link between soda consumption and oral cancer warrants further investigation, the emerging body of research raises important questions about the impact of dietary factors on oral health. Whether soda directly contributes to the development of oral cancer or serves as a marker for an overall unhealthy lifestyle, it is clear that reducing soda consumption and adopting a balanced diet are critical for maintaining oral health and preventing various chronic diseases.
It is essential for individuals to be mindful of their dietary choices and for healthcare providers to continue educating the public about the potential health risks associated with excessive soda consumption. By considering diverse perspectives and supporting further research in this field, we can work towards a better understanding of the complex relationship between soda and oral cancer, ultimately leading to more effective preventive strategies and improved public health outcomes.
Sources
- American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancers
- Journal of the American Medical Association, Physical Exercise and Physiologic Fitness