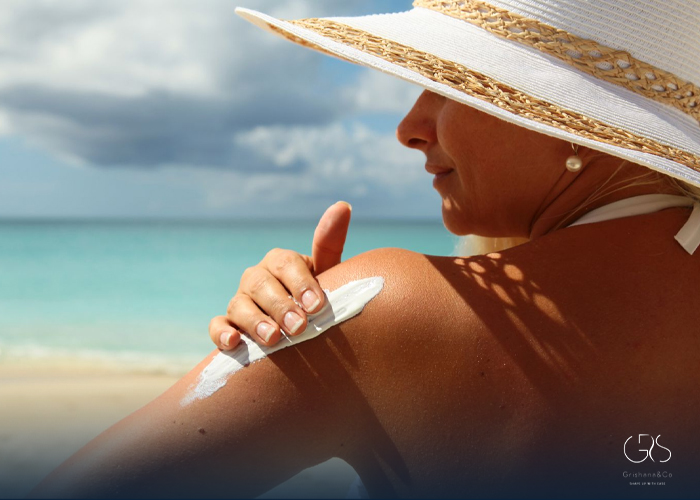
As the summer season approaches, many people are eager to spend more time outdoors, enjoying the sunshine and participating in various outdoor activities. However, the importance of protecting oneself from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation cannot be overstated. Exposure to UV rays from the sun can lead to skin damage, premature aging, and an increased risk of developing skin cancer. This raises the question: Should you ever go outside without sunscreen? What do dermatologists recommend in terms of sunscreen usage and the balance between sun protection and getting enough vitamin D from sunlight exposure?
The Importance of Sunscreen and Skin Protection
According to the American Cancer Society, skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, accounting for nearly half of all cancer cases. UV exposure is a leading cause of skin cancer, making it crucial to take measures to protect the skin from harmful rays. A 2014 study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that sunscreen use can reduce the risk of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, by 50 percent. This highlights the significant role that sunscreen plays in skin protection and reducing the risk of skin cancer.
Dermatologists emphasize the importance of wearing sunscreen whenever going outdoors, even on cloudy days or during winter months. UV rays can penetrate through clouds and windows, exposing the skin to potential damage. Dr. Debra Jaliman, a renowned dermatologist based in New York, emphasizes the need for daily sunscreen use to shield the skin from harmful UV radiation. In addition to sunscreen, protective clothing such as hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeve shirts can provide added protection against UV exposure.

The Connection Between Sunscreen and Vitamin D
While sunscreen is essential for protecting the skin, many individuals are concerned about the potential impact of sunscreen use on their vitamin D levels. Vitamin D is a vital nutrient that is synthesized in the skin in response to sunlight exposure. Adequate levels of vitamin D are important for various bodily functions, including maintaining bone health, immune function, and reducing the risk of certain diseases.
Dr. Jessica Wu, a dermatologist based in Los Angeles, points out that the body only needs a few minutes of sunlight exposure per day to produce enough vitamin D. While sunscreen can reduce the production of vitamin D in the skin, there are alternative sources of this essential nutrient. Foods such as fatty fish, eggs, and fortified products can help supplement vitamin D intake.
It’s crucial to strike a balance between protecting the skin from UV radiation and ensuring adequate vitamin D levels. Dr. Wu recommends being mindful of one’s skin type, the time of day, and the duration of sun exposure to optimize the benefits of sunlight while minimizing the risks of skin damage. For individuals concerned about vitamin D deficiency, supplementation may be a viable option to maintain optimal levels of this essential nutrient.
(I suggest reading my article to learn more about the benefits of Vitamin D)
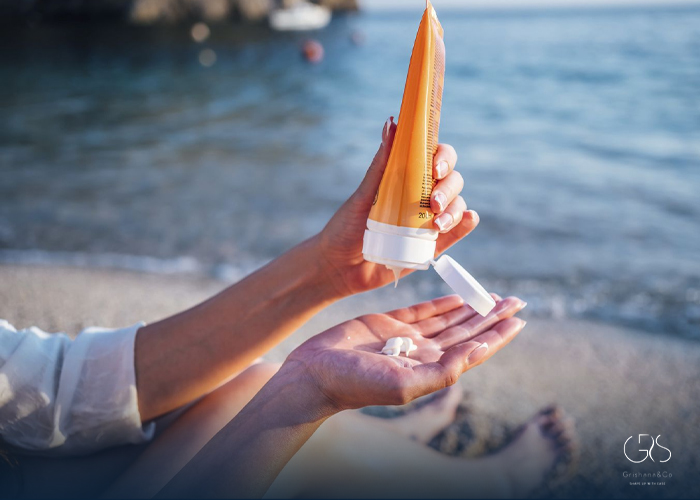

Is It Always Necessary to Wear Sunscreen While Outdoors?
The question of whether one should ever go outside without sunscreen depends on various factors, including individual skin type, time of day, and duration of sun exposure. People with fair skin, red or blonde hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible to UV damage and should take extra precautions when spending time outdoors. UV rays are strongest during midday, so shorter exposure times during those hours are advisable.
(Read more about skin types)
However, dermatologists caution against underestimating the potential harm of even brief sun exposure. Dr. Debra Jaliman emphasizes that UV rays can penetrate through clouds and windows, highlighting the need for sunscreen use regardless of weather conditions. The Skin Cancer Foundation reports that up to 80 percent of UV rays can pass through clouds, underscoring the importance of sun protection even on cloudy days.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher to shield the skin from both UVA and UVB rays. Proper application of sunscreen, using at least an ounce for each application and reapplying every two hours or more frequently when swimming or sweating, is essential for effective sun protection.
Conclusion: Finding the Balance
The debate on whether one should ever go outside without sunscreen underscores the importance of striking a balance between protecting the skin from UV radiation and ensuring adequate vitamin D levels. While sunscreen is the primary form of defense against harmful UV rays and skin damage, it’s essential to bear in mind that the body needs some sunlight exposure to produce vitamin D.
By considering individual factors such as skin type, time of day, and duration of sun exposure, individuals can optimize the benefits of sunlight while minimizing the risks of skin damage and vitamin D deficiency. Supplementing with vitamin D, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen as recommended by dermatologists are key strategies for maintaining skin health and overall well-being.
Sources
- American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Melanoma Skin Cancer
- WebMD, Vitamin D Deficiency
- The Skin Cancer Foundation, Sun-Protective Clothing