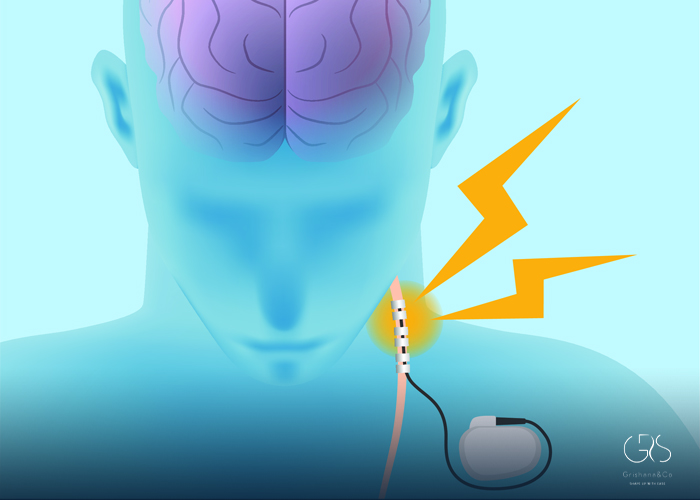
The vagus nerve, a vital component of our autonomic nervous system, extends from the brainstem to various organs throughout the body. Researchers have recently explored the therapeutic potential of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) in treating a variety of common conditions. By delivering electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, VNS has shown promising results in alleviating symptoms of epilepsy, depression, migraines, and inflammatory disorders. In this article, we delve into the mechanism and potential benefits of VNS, supported by relevant statistics and diverse perspectives.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Epilepsy:
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, affecting millions of people worldwide. Conventional treatment methods such as medication and surgery may not be effective for all patients. VNS, through its ability to modulate neural activity, has demonstrated notable success in reducing the frequency and severity of seizures, even in cases of drug-resistant epilepsy. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but researchers hypothesize that VNS-induced electrical impulses block or alter abnormal discharges in the brain.
Statistics: The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 65 million people worldwide live with epilepsy .
Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Depression:
Depression is a global mental health issue, and many individuals do not experience adequate relief from traditional treatments like medication and therapy. VNS has emerged as a potential alternative or adjunct treatment for depression. By modulating the brain’s neural circuits, VNS offers a promising approach to enhancing mood regulation. Studies have shown significant improvements in depressive symptoms among patients who have not responded well to other therapies, opening new avenues for managing treatment-resistant depression.
Statistics: The WHO reports that over 264 million people worldwide suffer from depression .
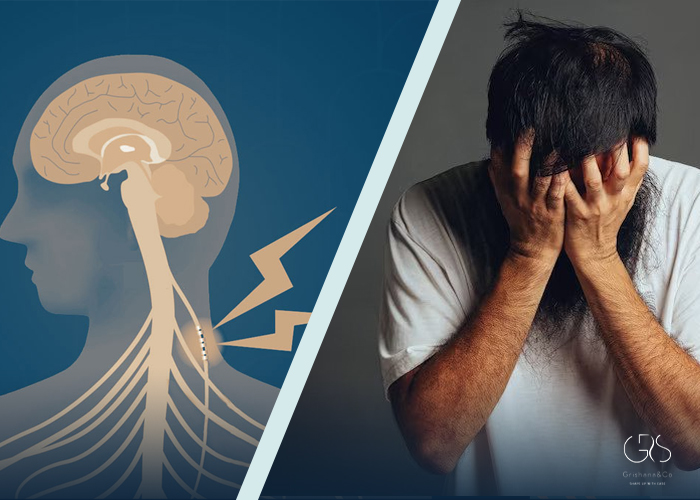

Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Migraines:
Migraines are debilitating headaches affecting millions of individuals globally. For individuals with chronic migraines unresponsive to medications, VNS has offered new hope. Research indicates that VNS can reduce the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraines, leading to an improved quality of life. The theory behind this is that VNS inhibits pain signals in the trigeminal nerve and modulates the brain’s response to pain, resulting in migraine relief.
Statistics: The Migraine Research Foundation estimates that migraines impact approximately 12% of adults globally .

Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Inflammatory Disorders:
Chronic inflammatory disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and asthma can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Cutting-edge research suggests that VNS might play a role in modulating inflammation. By activating anti-inflammatory pathways and regulating immune responses, VNS shows potential for alleviating symptoms and reducing the impact of inflammatory disorders.
While the exact mechanism is still under investigation, preliminary studies indicate positive outcomes for VNS in managing these conditions.
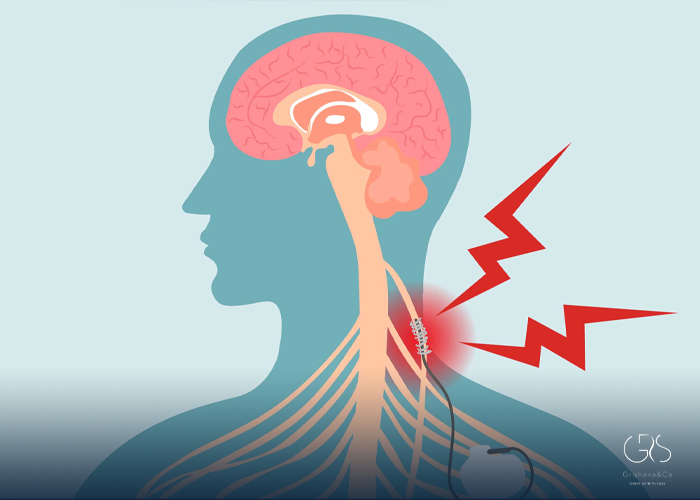
Conclusion:
The emerging field of vagus nerve stimulation holds immense potential in revolutionizing the treatment landscape for epilepsy, depression, migraines, and inflammatory disorders. By modulating neural activity through electrical impulses delivered to the vagus nerve, VNS has shown promise in providing relief and enhancing quality of life for patients. Nonetheless, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the suitability and effectiveness of VNS in individual cases.
Through ongoing research and diverse perspectives, VNS may pave the way for more effective and personalized treatment options for these common conditions.
Sources
- World Health Organization, Epilepsy
- Migraine Research Foundation, Migraine research