Obesity continues to be a prevailing issue in America, with nearly 42.4% of the adult population categorized as obese as of 2017-2018, according to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) [1]. For individuals struggling with obesity, weight loss medications can be a beneficial addition to diet and exercise regimens. However, it is essential to understand which medications are FDA-approved for weight loss, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects.
There are several FDA-approved medications for long-term weight management. These medications target different pathways in the body to promote weight loss and may be suitable for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, or 27 with at least one weight-related comorbidity. They should be utilized under the guidance of a healthcare provider after lifestyle modifications have been unsuccessful in achieving weight loss goals.
Some of the FDA-approved weight loss medications include:
- Orlistat (Xenical): Orlistat works by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. It is typically taken three times a day with meals and has been shown to aid in weight loss when combined with a reduced-calorie diet .
- Phentermine-Topiramate (Qsymia): Qsymia is a combination of phentermine, an appetite suppressant, and extended-release topiramate, which is believed to make individuals feel full. It has been approved for long-term weight management and can aid in weight loss when used alongside a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): Saxenda is a GLP-1 receptor agonist administered through a once-daily injection. It works by regulating appetite, leading to reduced caloric intake and subsequent weight loss. It has been approved for weight management in individuals with obesity or who are overweight and have at least one weight-related comorbidity.
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Wegovy is a recently approved, high-dose form of the diabetes medication semaglutide. It has shown significant weight loss effects in clinical trials and is administered through a weekly injection.
- Tirzepatide (Zepbound): Tirzepatide is a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that has shown potential for weight loss and improved glycemic control in clinical trials. It is administered through a once-weekly injection and is being evaluated for its efficacy and safety .
- Setmelanotide (Imcivree): Imcivree is a drug used for individuals with obesity due to genetic conditions that affect the appetite and hunger signaling pathways. It has been approved for the treatment of obesity and control of hunger associated with genetic conditions in adults and children over 6 years old.
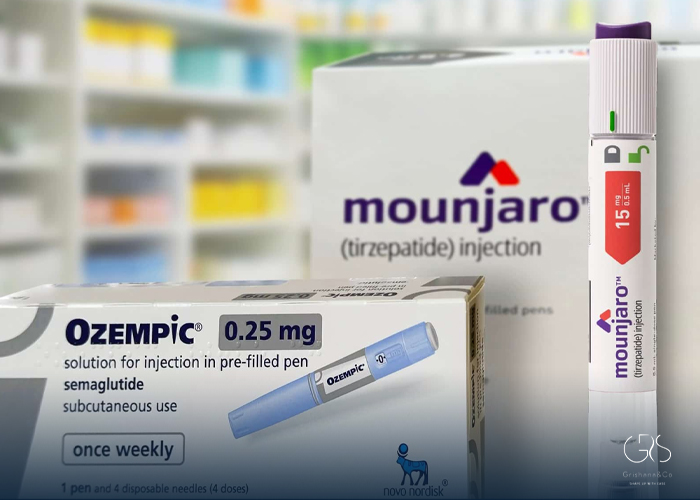
- Mounjaro (Tirzepatide): Tirzepatide is a once-weekly injectable medication that combines the actions of two different hormones, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). It works by regulating appetite, glucose metabolism, and body weight. Clinical trials have shown promising results for weight loss and improved glycemic control.
8.Ozempic (Semaglutide): Semaglutide is another GLP-1 receptor agonist that was initially approved for diabetes management. However, recent studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in promoting weight loss. It is administered as a once-weekly injection and has shown significant reduction in body weight in individuals with obesity or overweight .
When considering weight loss medications, it is crucial to discuss with a healthcare provider to evaluate the risks and benefits and determine the most suitable option based on individual health conditions and weight loss goals. Moreover, pharmaceutical interventions should be complemented by lifestyle modifications such as diet modification, physical activity, and behavioral therapy to optimize weight loss results and ensure long-term success.
Additionally, apart from pharmaceutical interventions, there are other effective ways to support weight loss efforts:
Diet Modification: Incorporating a balanced, reduced-calorie diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can facilitate weight loss.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise, including both aerobic and strength training, plays a vital role in achieving and maintaining weight loss and overall health.
Behavioral Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral interventions and counseling can help individuals make sustainable lifestyle changes and manage emotional eating.
Conclusion:
FDA-approved weight loss medications such as Orlistat, Qsymia, Saxenda, Wegovy, Zepbound , Imcivree, Mounjaro, and Ozempic can be valuable tools for individuals struggling with obesity. These medications, along with emerging drugs, offer a range of options for individuals pursuing weight management. However, integrating lifestyle modifications and individualized medical supervision is essential for comprehensive management of obesity and achieving sustainable weight loss.
Sources
- Newer Medications for Weight Loss, Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
- Mayo Clinic, Prescription weight-loss drugs
- Healthline, Are Weight Loss Medications Effective? A Dietitian Explains