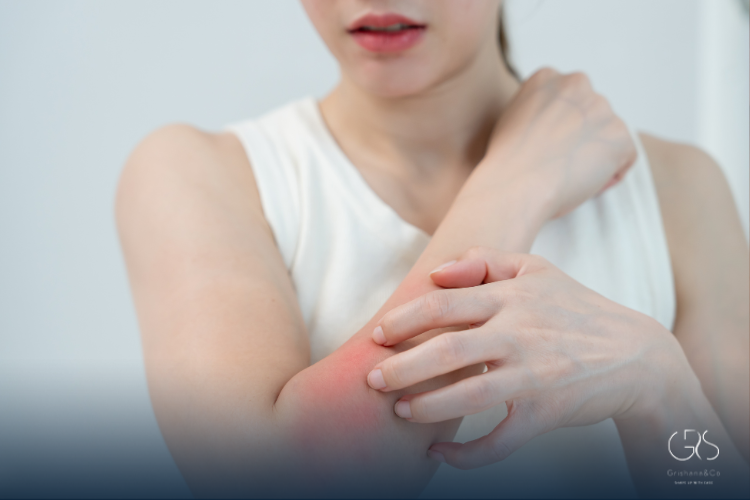
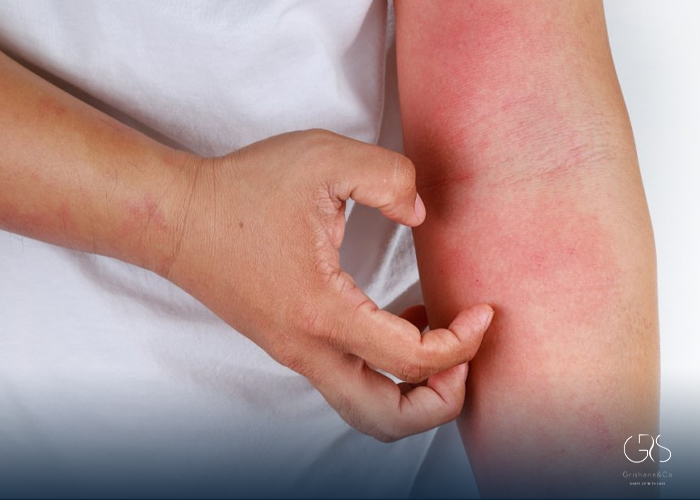
Skin rashes caused by allergies are incredibly common, yet often confusing. One day your skin feels normal, and the next it’s red, itchy, swollen, or covered in bumps. Understanding what’s happening beneath the surface can make allergy rash treatment far more effective and much less stressful. This guide explains the science behind allergic rashes, why they happen, how to identify different types, and which treatments are proven to work.
What Is an Allergy Rash?
An allergy rash is a skin reaction triggered when your immune system overreacts to a substance it considers harmful, even if it isn’t dangerous. These substances, known as allergens, can include foods, medications, plants, metals, cosmetics, or environmental factors. The immune system releases chemicals like histamine, leading to inflammation, itching, redness, and swelling. Effective allergy rash treatment focuses on calming this immune response while protecting the skin barrier.
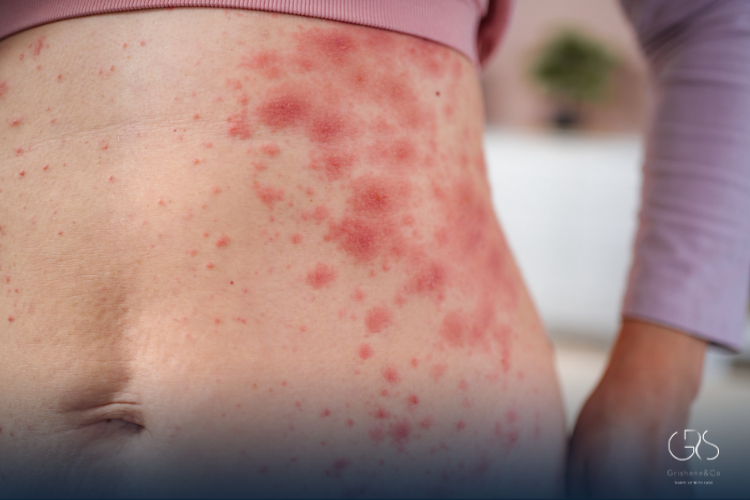
How the Immune System Triggers Skin Reactions
When an allergen contacts the skin or enters the body, immune cells called mast cells release histamine and inflammatory mediators. This increases blood vessel permeability, causing redness and swelling, and stimulates nerve endings, leading to itching. Scientific studies show that histamine plays a central role in allergic skin reactions, which is why many allergy rash treatment options target histamine pathways.
Common Types of Allergy Rashes
Not all allergic rashes look or behave the same. Identifying the type is essential for choosing the right allergy rash treatment.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin touches an allergen such as nickel, latex, fragrances, or poison ivy. The rash usually appears exactly where contact happened and may cause redness, blisters, or scaling.
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives are raised, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body and often move around. They are frequently triggered by foods, medications, infections, or stress.
Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Triggers
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic condition with a strong allergic component. Environmental allergens, dust mites, and certain foods can worsen symptoms.
Drug-Induced Allergy Rashes
Some medications, including antibiotics and anti-seizure drugs, can trigger allergic rashes. These may range from mild redness to severe, life-threatening reactions requiring immediate medical care.
Causes and Risk Factors Behind Allergy Rashes
Understanding the cause is the foundation of long-term allergy rash treatment.
Environmental Allergens
Pollens, mold spores, animal dander, and dust mites can trigger rashes in sensitive individuals, especially those with a history of allergies or asthma.

Food-Related Allergic Skin Reactions
Foods such as peanuts, shellfish, eggs, and milk can cause skin rashes, sometimes alongside digestive or respiratory symptoms.
Chemical and Cosmetic Exposure
Soaps, detergents, preservatives, and hair or skin products often contain allergens that disrupt the skin barrier and provoke inflammation.
Genetic and Lifestyle Factors
Research shows that people with a family history of allergies are more prone to allergic skin reactions. Stress, poor sleep, and a damaged skin barrier can also increase susceptibility.
Allergy Rash Treatment Options Backed by Science
Effective allergy rash treatment usually involves a combination of avoiding triggers, calming inflammation, and restoring the skin barrier.
Antihistamines for Allergy Rash Treatment
Oral antihistamines such as cetirizine, loratadine, and diphenhydramine block histamine receptors and reduce itching, redness, and swelling. Clinical trials confirm their effectiveness in managing acute allergic rashes and hives.
Topical Corticosteroids
Low- to medium-potency corticosteroid creams reduce inflammation and itching by suppressing immune activity in the skin. They are a cornerstone of allergy rash treatment when used correctly and for limited durations.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Creams
Topical calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are alternatives for sensitive areas such as the face and eyelids, especially in chronic conditions like eczema.
Natural and Supportive Allergy Rash Treatment Approaches
While medications are often necessary, supportive measures can significantly improve comfort and healing.
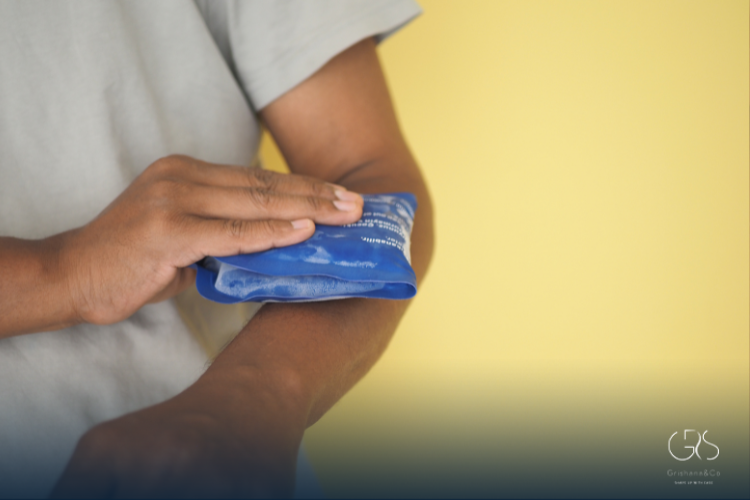
Cold Compresses and Skin Cooling
Applying a cool compress reduces blood flow to the inflamed area and temporarily relieves itching and swelling.

Moisturizers and Barrier Repair
Using fragrance-free emollients helps restore the skin barrier, reducing allergen penetration and supporting long-term allergy rash treatment.
Oatmeal and Soothing Baths
Colloidal oatmeal baths are supported by dermatological research for their anti-inflammatory and skin-soothing properties.

When Allergy Rash Treatment Requires Medical Care
Some allergic rashes should never be managed at home.
Warning Signs of Severe Allergic Reactions
Seek urgent medical attention if a rash is accompanied by facial swelling, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or rapid spreading. These may signal anaphylaxis.
Chronic or Recurrent Rashes
If rashes persist for weeks or keep returning, a dermatologist or allergist may recommend patch testing, blood tests, or advanced allergy rash treatment strategies.
Preventing Future Allergy Rashes
Prevention is a crucial part of effective allergy rash treatment.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Keeping a symptom diary can help identify patterns related to foods, products, or environments.
Strengthening the Skin Barrier
Daily use of gentle cleansers and moisturizers reduces flare-ups by maintaining healthy skin defenses.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Managing stress, improving sleep, and maintaining a balanced diet can reduce immune overactivity and improve skin health.
Allergy Rash Treatment in Children and Sensitive Skin
Children and individuals with sensitive skin require special care.
Pediatric Considerations
Children’s skin absorbs medications more easily, so lower-potency treatments and medical supervision are essential.
Safe Allergy Rash Treatment for Sensitive Areas
The face, groin, and skin folds require gentle treatments to avoid thinning or irritation.
Conclusion
Allergic skin rashes can be uncomfortable, frustrating, and sometimes alarming, but they are highly manageable with the right approach. Understanding how the immune system reacts, recognizing different types of rashes, and choosing evidence-based allergy rash treatment options can dramatically improve outcomes. Whether the solution involves antihistamines, topical therapies, lifestyle changes, or medical guidance, early and informed action is key. With science-backed care and thoughtful prevention, most people can achieve healthy, comfortable skin and prevent future flare-ups.
Sources
- American Academy of Dermatology Association, Rashes
- American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, Skin Allergy
- WebMD, Skin Allergies and Contact Dermatitis: The Basics