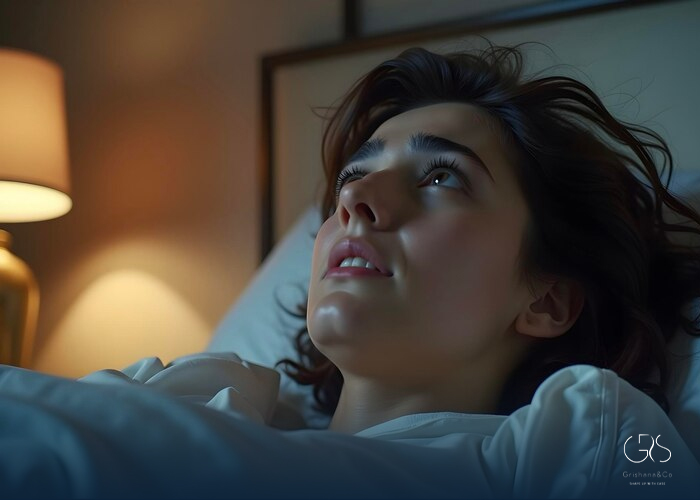
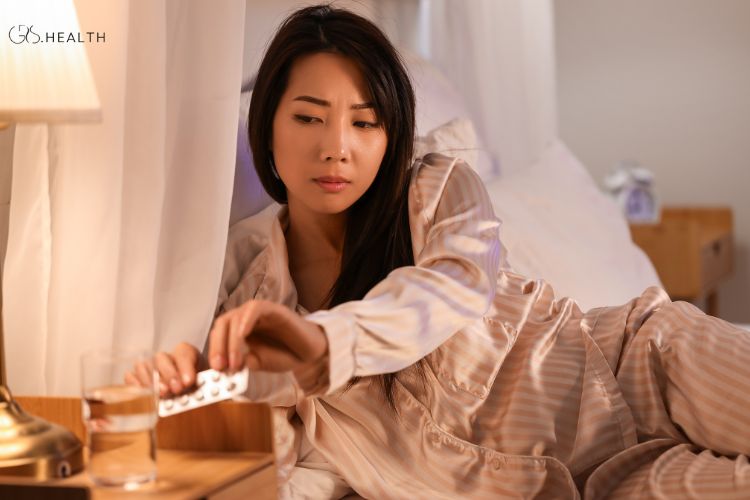
Waking up with anxiety in the middle of the night is a distressing experience that affects a significant number of individuals. Nocturnal anxiety, as it is commonly referred to, can have profound impacts on one’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. This article aims to explore the phenomenon of waking up with anxiety, including the prevalence of this experience, its various causes, and strategies for coping with it. Additionally, it will consider diverse perspectives to highlight the different ways in which individuals from various backgrounds may experience and cope with nocturnal anxiety.
Prevalence and Statistics
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health issues globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 264 million people suffer from anxiety disorders worldwide. While specific statistics on nocturnal anxiety are not readily available, a significant portion of those affected by anxiety disorders experience symptoms that disrupt their sleep, leading to waking up with anxiety in the middle of the night.
Additionally, research from the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) indicates that anxiety disorders affect approximately 40 million adults in the United States, making it a prevalent issue in the country. It is important to note that these statistics may not fully capture the extent of nocturnal anxiety, as many individuals may not seek treatment for their symptoms or may not have been formally diagnosed with an anxiety disorder.
Understanding Nocturnal Anxiety
Nocturnal anxiety can present in various ways, including feelings of fear, unease, or worry upon waking up in the middle of the night. Individuals may experience racing thoughts, heart palpitations, sweating, and an overall sense of dread or impending doom. These symptoms can significantly disrupt sleep, leading to insomnia, fatigue, and impaired daytime functioning.

Causes and Contributing Factors
There are numerous factors that can contribute to the development of nocturnal anxiety. Chronic stress, trauma, genetic predisposition, and imbalances in brain chemistry are commonly cited as underlying causes. Additionally, external stressors such as work pressure, economic uncertainty, or societal issues can play a significant role in triggering and exacerbating nocturnal anxiety.
From a biological perspective, disruptions in the body’s stress response system, including the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, can lead to heightened anxiety symptoms, particularly during vulnerable periods such as the middle of the night. Furthermore, individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders or other mental health conditions may be more susceptible to experiencing anxiety during sleep.
(Read more about the causes of anxiety)
Impact on Mental and Physical Health
The impact of waking up with anxiety in the middle of the night can have far-reaching effects on an individual’s well-being. Sleep disturbances due to anxiety can contribute to chronic insomnia, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, and impaired cognitive function. Prolonged periods of disrupted sleep can also exacerbate existing anxiety symptoms, creating a cycle of sleeplessness and heightened anxiety.
Furthermore, research published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research emphasizes the negative impact of disrupted sleep on emotional regulation, potentially exacerbating anxiety symptoms and impairing an individual’s ability to cope with stress.

Diverse Perspectives
Nocturnal anxiety affects individuals from diverse backgrounds, and it is essential to consider the varied experiences and coping strategies within different communities. Cultural, socioeconomic, and racial factors can influence how individuals perceive and manage anxiety, including waking up with anxiety in the middle of the night.
For example, individuals from marginalized communities may face additional stressors and barriers to accessing mental health resources, potentially exacerbating their experiences of nocturnal anxiety. Additionally, cultural beliefs and practices surrounding sleep and anxiety may influence how individuals from different backgrounds perceive and cope with nocturnal anxiety.
Understanding and considering these diverse perspectives is crucial for developing comprehensive and inclusive approaches to supporting individuals affected by nocturnal anxiety.
Coping Strategies and Support
Managing and coping with waking up with anxiety in the middle of the night requires a multifaceted approach. Seeking professional help from mental health practitioners, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, or licensed therapists, is essential for addressing underlying anxiety disorders and developing personalized treatment plans.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown to be effective in treating anxiety disorders, including those that manifest during sleep. CBT can help individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns, develop relaxation techniques, and implement strategies to improve sleep quality.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms, particularly if the nocturnal anxiety is severe or persistent. However, it is important for individuals to work closely with healthcare providers to understand the potential benefits and risks of any prescribed medications.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness and deep breathing exercises, can complement clinical interventions and contribute to better sleep and reduced anxiety symptoms.
Furthermore, building a strong support network and seeking understanding from friends, family, or support groups can provide invaluable emotional support for individuals experiencing nocturnal anxiety. Peer support and validation of one’s experiences can reduce feelings of isolation and help individuals feel more empowered to manage their symptoms.
Conclusion
Waking up with anxiety in the middle of the night is a complex and challenging experience that can significantly impact one’s well-being. By understanding the prevalence, causes, and diverse perspectives related to nocturnal anxiety, society can work towards developing more inclusive and effective approaches to support individuals affected by this phenomenon. Promoting awareness, access to mental health resources, and cultural sensitivity can contribute to a more supportive environment for those navigating the challenges of waking up with anxiety.
Sources
- World Health Organization (WHO), Mental disorders
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA), Anxiety Disorders - Facts & Statistics
- Sleepfoundation, Anxiety at Night
- Mayoclinic, Nocturnal panic attacks