Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant emotional distress and impacting self-confidence. There are various types of hair loss, each requiring specific treatments tailored to address the underlying causes. In this article, we will explore expert-approved treatments for the six main types of hair loss, backed by relevant statistics and diverse perspectives.
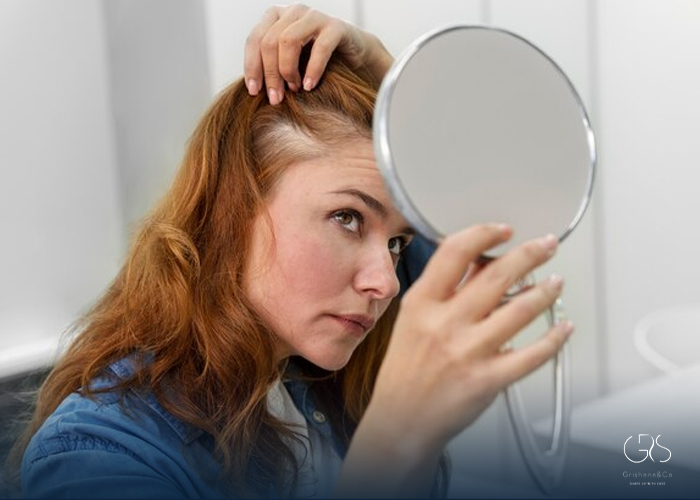
1.Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness):
The most common form of hair loss, androgenetic alopecia, affects both men and women. Treatments approved by experts include minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) for men. These medications have shown effective results in stimulating hair growth and preventing further hair loss. For women, minoxidil is also recommended, along with low-level laser therapy (LLLT), which stimulates hair follicles.
2.Alopecia Areata:
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition resulting in patchy hair loss. Corticosteroids, either applied topically or injected into the affected areas, are commonly prescribed to help stimulate hair regrowth. Another alternative is topical immunotherapy, utilizing chemicals like diphencyprone (DPCP) to provoke an allergic response and prompt hair regrowth.
3.Telogen Effluvium:
Telogen effluvium is a temporary hair loss condition resulting from physical or emotional stress. The main focus of treatment is managing the underlying stressor. Experts suggest stress reduction techniques such as meditation, exercise, and counseling, coupled with a balanced diet. Supplements like biotin and iron may also support hair regrowth. Once the stressor is resolved, hair typically grows back within a few months.

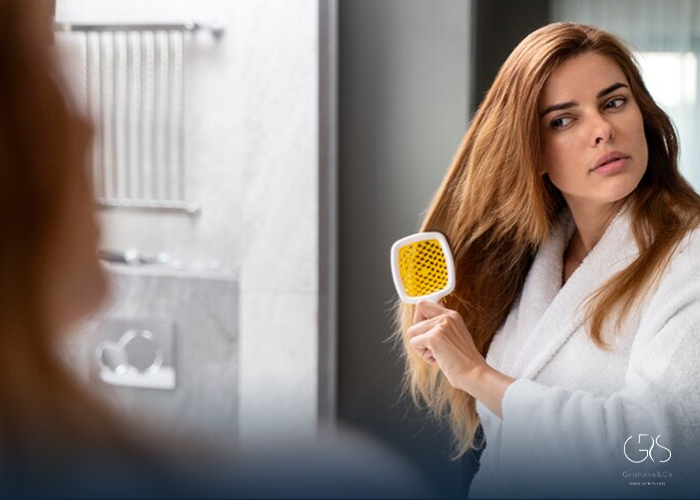
4.Traction Alopecia:
Traction alopecia occurs due to prolonged tension on the hair from hairstyles like tight braids or weaves. Experts recommend avoiding such hairstyles and allowing the hair to rest and recover. Additionally, using Minoxidil and hair supplements can assist in stimulating hair regrowth. In extreme cases, hair transplant surgery may be considered.

5.Trichotillomania:
Trichotillomania is a psychiatric disorder characterized by compulsive hair pulling. Treatment involves a multi-disciplinary approach, combining therapy with cognitive-behavioral techniques, medications (such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), and habit-reversal training. Support groups and counseling play a vital role in helping individuals overcome this condition.
6.Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia:
Chemotherapy drugs often cause hair loss as a side effect. Scalp cooling devices, also known as cold caps, have shown promise in reducing chemotherapy-induced hair loss by constricting blood vessels in the scalp, limiting the drug’s reach to the hair follicles. Minoxidil and LLLT can also be used alongside scalp cooling.
Conclusion:
Hair loss can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life, but expert-approved treatments exist for each specific type of hair loss. By understanding the underlying causes and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can regain their confidence and restore their hair. Remember, it is always essential to consult with a dermatologist or a healthcare professional to identify the most suitable treatment for your type of hair loss.
Sources
- American Academy of Dermatology Association, Hair Loss: Who Gets and Causes
- Mayo Clinic, Hair loss
- British Association of Dermatologists, Alopecia Areata
- American Hair Loss Association, Telogen Effluvium
- American Academy of Dermatology Association, Hair loss: Diagnosis and treatment
- WebMD, Chemotherapy and Hair Loss: Cold Caps, Scalp Cooling, and More