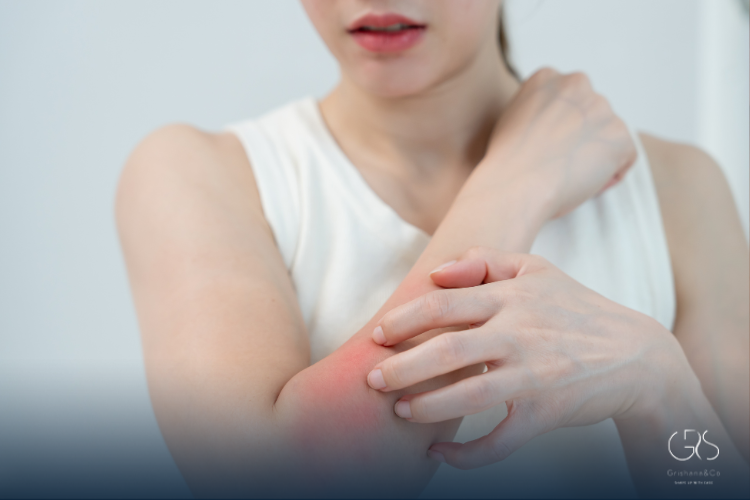
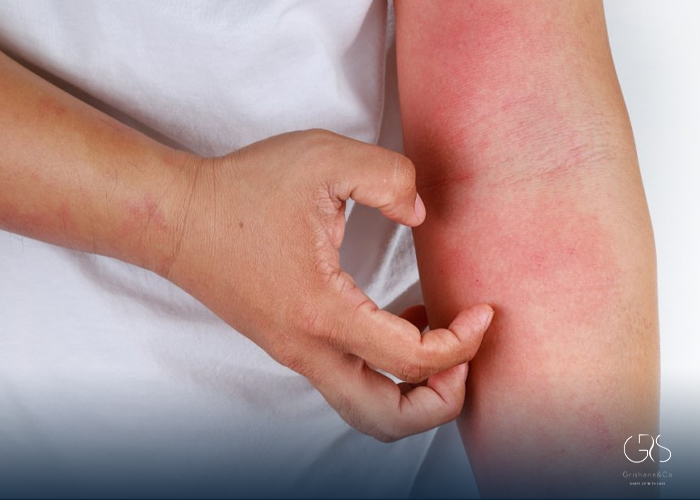
Seasonal allergies symptoms, alternatively referred to as allergic rhinitis or hay fever, are a prevalent health issue impacting millions globally. These allergic reactions occur when the immune system reacts excessively to environmental substances known as allergens. Although some individuals may endure allergies throughout the year, many experience seasonal allergies symptoms that intensify during specific periods, like spring or fall.
What Causes Seasonal Allergies?
Seasonal allergies are typically triggered by airborne allergens such as pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds. When these allergens are inhaled, the immune system perceives them as harmful invaders and releases chemicals like histamine to fight them off. This immune response can lead to various symptoms, including sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and throat irritation.
While pollen is a common trigger for seasonal allergies, other allergens such as mold spores and dust mites can also contribute to allergic reactions. Factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental exposure can influence an individual’s susceptibility to seasonal allergies.
(Read more about dust mite allergies)
Symptoms of Seasonal Allergies
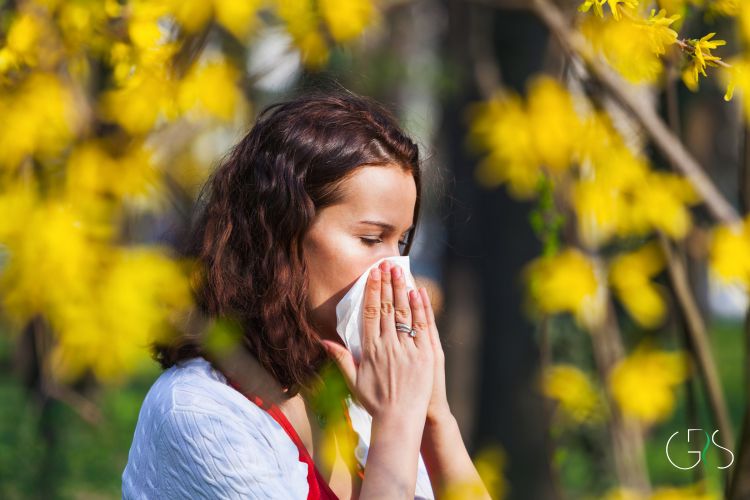
Seasonal allergies can manifest in a variety of symptoms, which may vary in severity from person to person. Common symptoms of seasonal allergies include:
- Sneezing: Frequent and uncontrollable sneezing is a typical symptom of seasonal allergies.
- Runny or Stuffy Nose: Nasal congestion or a runny nose can be a result of the body’s reaction to allergens.
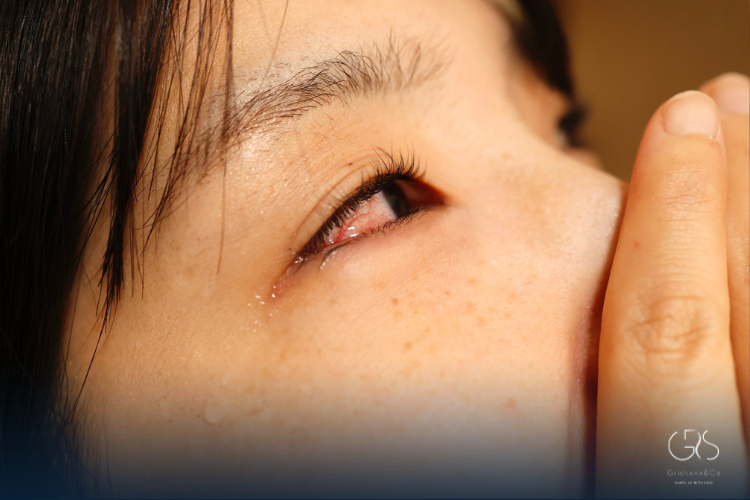
- Itchy, Watery Eyes: Red, itchy, and watery eyes are often a sign of allergic conjunctivitis.
- Throat Irritation: Scratchy throat or throat clearing may occur due to postnasal drip.
- Fatigue: Allergies can cause fatigue and affect overall energy levels.
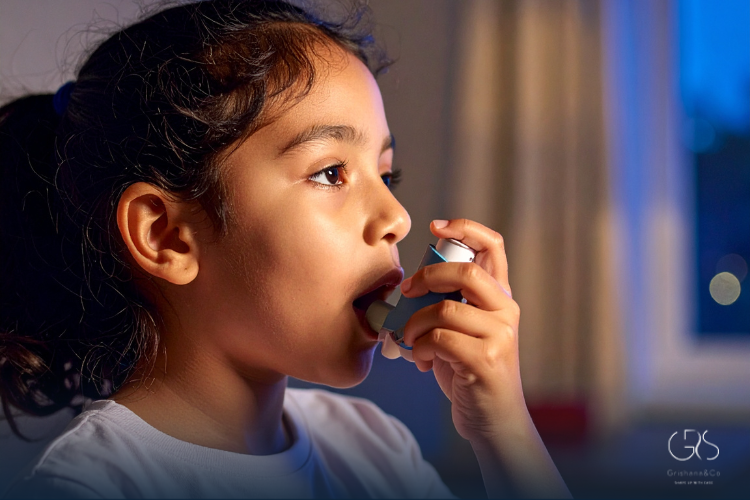
In severe cases, seasonal allergies can trigger asthma symptoms in individuals with asthma, leading to wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Managing Seasonal Allergies
Managing seasonal allergies involves a combination of prevention strategies, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments. Here are some tips to help alleviate seasonal allergy symptoms:
- Avoiding Allergens: Try to minimize exposure to pollen by staying indoors on high pollen days, keeping windows closed, and using air purifiers.
- Using Allergy Medications: Over-the-counter antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal sprays can help relieve symptoms. Prescription medications or allergy shots may be necessary for severe cases.
- Allergy-proofing Your Home: Regularly clean and dust your home, wash bedding in hot water, and use allergen-proof covers on pillows and mattresses.
- Nasal Irrigation: Using a saline solution to rinse the nasal passages can help reduce congestion and improve breathing.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help thin mucus and alleviate nasal congestion.
- Consulting a Doctor: If symptoms persist or worsen despite home remedies, consult an allergist or healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan.
Diverse Perspectives on Seasonal Allergies
Seasonal allergies can impact individuals across different age groups, backgrounds, and regions. It is essential to consider diverse perspectives when discussing seasonal allergies to address the unique challenges faced by various populations.
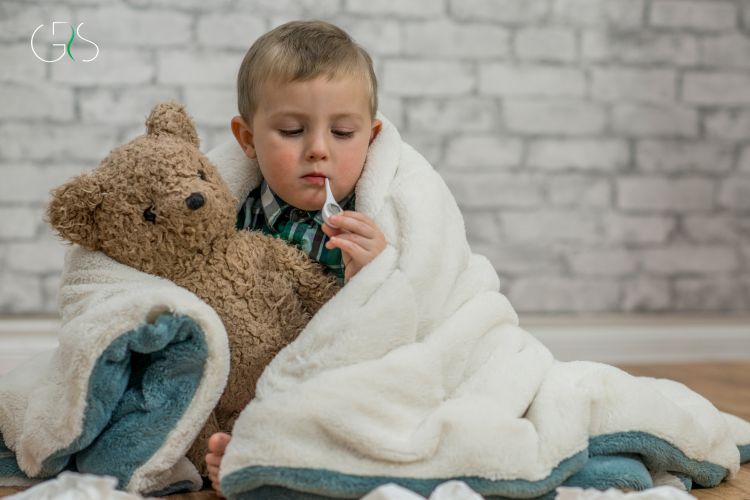
Children and Seasonal Allergies
Children can be particularly vulnerable to seasonal allergies, as their immune systems are still developing. Symptoms of seasonal allergies in children may manifest differently than in adults, with younger children experiencing more nasal congestion and ear infections. Parents and caregivers should be vigilant about managing their children’s allergies to ensure proper symptom relief and improve quality of life.

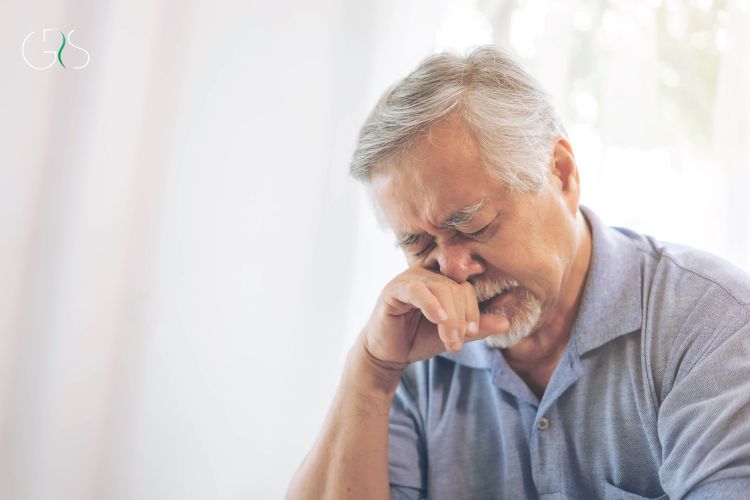
Elderly Individuals and Seasonal Allergies
Older adults may be more susceptible to seasonal allergies due to age-related changes in the immune system. Seasonal allergies can exacerbate existing health conditions in elderly individuals, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Healthcare providers working with older patients should consider these factors when diagnosing and treating seasonal allergies in this population.

Work Environment and Seasonal Allergies
For individuals working in outdoor or agricultural settings, seasonal allergies can significantly impact their productivity and well-being. Employers should provide resources and accommodations to support employees with seasonal allergies, such as flexible work schedules during peak pollen seasons or access to allergen-reducing equipment.
Socioeconomic Factors and Seasonal Allergies
Access to healthcare, medications, and allergy testing can vary based on socioeconomic status, leading to disparities in the management of seasonal allergies. Community outreach programs, public health initiatives, and insurance coverage for allergy treatments can help bridge these gaps and ensure that everyone has access to proper care.
Conclusion
Seasonal allergies are a prevalent health issue that affects individuals of all ages and backgrounds. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for seasonal allergies, we can work towards improving the quality of life for those living with this condition. Through a holistic approach that considers diverse perspectives, we can better address the unique challenges faced by different populations in managing seasonal allergies effectively.
Sources
- American College of Allergy, Hay Fever
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Allergies