Accidents happen, and head injuries are a common consequence of such incidents. Whether it’s a slip and fall or a sports-related collision, knowing how to respond to a head injury is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcome. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of head injuries, including their types and associated symptoms, as well as steps to take after sustaining a head injury.
What Is a Head Injury?
A head injury refers to any trauma or injury to the skull, scalp, brain, or surrounding tissues. It can range from mild to severe and can have both short-term and long-term effects on an individual’s health.
Types of Head Injuries
There are various types of head injuries that can occur, each with its own characteristics and potential complications. These include:
Brain Contusion
A brain contusion occurs when there is bruising of the brain tissues. It occurs due to the forceful impact of the brain against the skull, resulting in localized bleeding and swelling. Severe contusions may require surgical intervention.
Concussion
A concussion is a type of mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occurs due to a blow to the head or a sudden jolt to the body that causes the brain to move rapidly back and forth within the skull. Concussions are common in sports-related activities and may not always involve loss of consciousness.
Hematoma
A hematoma refers to the pooling of blood outside the blood vessels. When it occurs within the brain, it is known as an intracerebral hematoma. Hematomas can increase pressure on the brain and require immediate medical attention.
Minor Head Injury
A minor head injury refers to a mild injury that does not involve any significant damage to the brain. Symptoms may include a headache, dizziness, or confusion. While they are generally not life-threatening, it is essential to monitor symptoms closely and seek medical attention if they worsen.

Skull Fracture
A skull fracture occurs when one or more bones of the skull break. It can vary in severity and location and may require immediate medical attention depending on the extent of the fracture.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
A traumatic brain injury refers to any injury caused by an external force that affects the structure or function of the brain. TBIs can range from mild to severe and may have long-term cognitive, physical, and emotional effects.
Symptoms and Causes of Head Injuries
Head injuries can present a wide range of symptoms depending on the type and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Memory problems
- Slurred speech
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in behavior or mood
- Loss of consciousness (in severe cases)
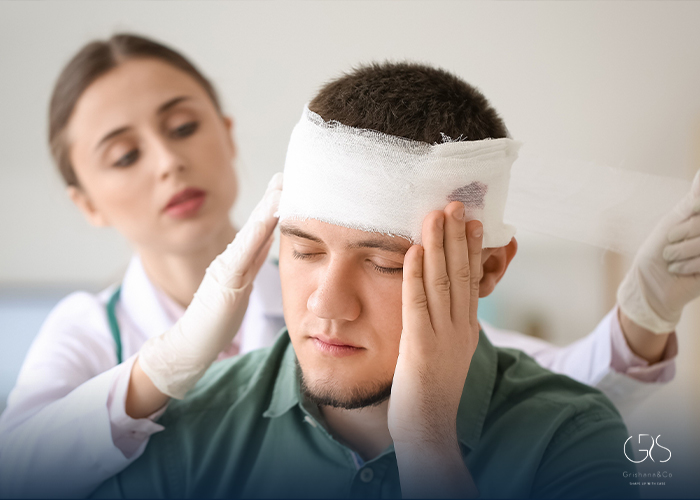
Head injuries can occur due to various causes, including:
- Falls
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Sports-related injuries
- Physical assaults
- Workplace accidents
It is important to note that head injuries can affect individuals differently based on their age, overall health, and individual susceptibility. Understanding and respecting diverse perspectives can facilitate appropriate care and support for those who have experienced head trauma.
What To Do After Hitting Your Head
Knowing how to respond promptly and appropriately after hitting your head is crucial to minimize the potential risks associated with head injuries. Here are some steps to follow:
First Aid
- Assess the Situation: Immediately after hitting your head, take a moment to assess the severity of the injury. Look for signs of a concussion such as dizziness, nausea, confusion, or loss of consciousness. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention right away.
- Rest and Monitor Symptoms: It’s important to rest and avoid any strenuous activities after a head injury. Monitor your symptoms carefully over the next 24 hours for any changes or worsening conditions. If symptoms persist or get worse, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
- Apply Ice: To reduce swelling and alleviate pain, apply an ice pack to the area where you hit your head. Be sure to wrap the ice pack in a cloth to prevent direct contact with your skin, and only apply it for short intervals at a time.
- Keep a Record: Keep a detailed record of the incident, including how it happened, any symptoms you experience, and when they occur. This information will be valuable when seeking medical advice or treatment.
When To Get Immediate Medical Attention
While many head injuries can be managed at home with rest and monitoring, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. These include:
- Persistent or worsening headaches
- Repeated vomiting
- Seizures
- Weakness or numbness in the extremities
- Slurred speech or difficulty understanding speech
- Changes in behavior or personality
If any of these symptoms occur, seek immediate medical assistance as they may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Treatment and How To Care For a Head Injury at Home
The treatment for head injuries will depend on the type and severity of the injury. In mild cases, rest and over-the-counter pain medication may be sufficient. However, more severe injuries may require medical intervention, such as stitches for wounds, medication for pain management, or surgery in severe cases.
If you are caring for a head injury at home, it’s important to:
- Monitor Symptoms: Continuously monitor the individual for changes in symptoms or any alarming signs that may require immediate medical attention.
- Rest and Relax: Encourage the injured person to rest and avoid strenuous activities that could exacerbate their symptoms.
- Provide Support: Offer emotional support as well as assistance with daily activities as needed.
- Follow Medical Advice: If a healthcare professional has provided specific instructions or medication, ensure they are followed carefully.

Preventing Head Injuries
Preventing head injuries is crucial in reducing the occurrence and severity of such incidents. Some preventive measures include:
- Wearing appropriate protective gear (such as helmets) during sports and recreational activities.
- Maintaining a safe environment at home and work by minimizing hazards and implementing safety measures.
- Being cautious while engaging in activities that could pose a risk of falls or head impacts.
- Educating oneself and others about the importance of safety precautions and prompt medical attention in the event of a head injury.
Conclusion
Head injuries are a serious matter that requires attention and care. By understanding the different types and symptoms of head injuries, and by following the appropriate steps after sustaining a head injury, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their well-being or that of someone else who has experienced a head injury.
Sources
- CDC, Traumatic Brain Injury.
- Mayo Clinic, Concussion