Maintaining good oral health is crucial for overall well-being. While dental hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups play a significant role, emerging research suggests a potential link between weight and gum disease. This article delves into the complex relationship between weight and gum disease, shedding light on the topic based on insights from dietitians, supported by relevant statistics, and incorporating diverse perspectives.
I. Understanding Gum Disease:
Before exploring the connection between weight and gum disease, one must comprehend the basics of gum disease itself. Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, encompasses various conditions affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. These conditions can range from mild inflammation (gingivitis) to more severe cases of periodontitis.
II. The Interplay: Weight and Gum Disease:
A. Exploring the Link with Obesity:
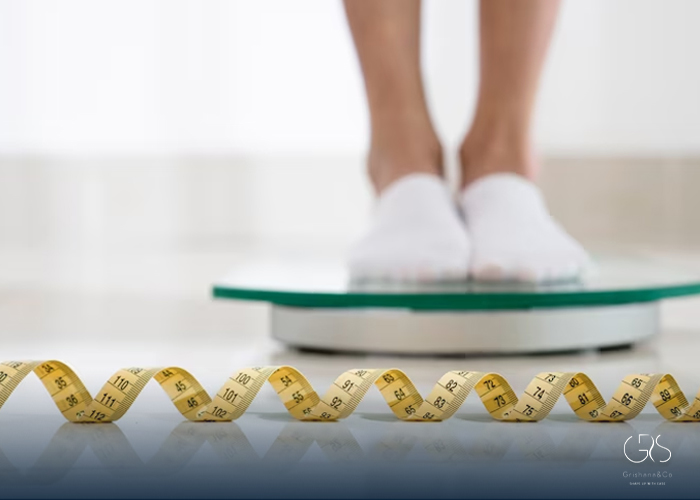

Statistics: Cite relevant statistics indicating a higher prevalence of gum disease among individuals with obesity, and suggest that further research is needed to explore this relationship.
The Mechanisms: Elaborate on potential biological and lifestyle factors that contribute to the increased risk of gum disease in individuals with obesity, such as inflammation, insulin resistance, and dietary choices.
Adipose Tissue Inflammation: Discuss the impact of chronic inflammation associated with obesity and its potential correlation with periodontal inflammation.
B. Delving into Underweight and Gum Disease:
The Under-Researched Aspect: Shed light on the limited research surrounding the connection between being underweight and gum disease, despite the importance of addressing this aspect in a comprehensive analysis.
Malnutrition and Gum Health: Highlight the potential effects of malnutrition, inadequate nutrient intake, and associated immune system compromises on gum health.

III. The Role of Diet and Nutritional Factors:
A. Sugar and Its Implications:
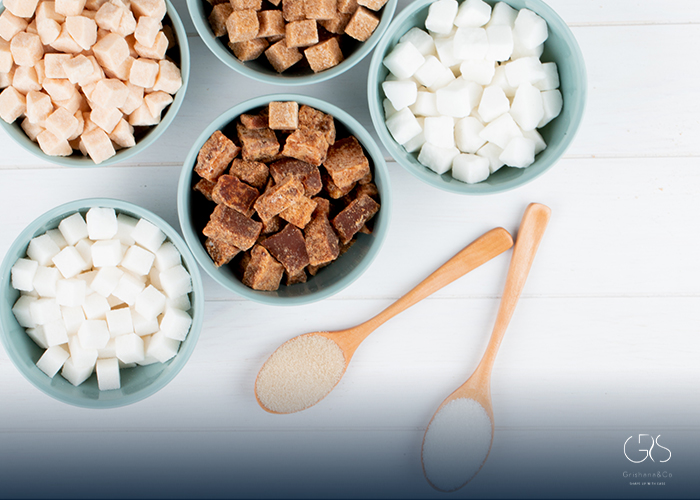

The Sugar-Dental Health Relationship: Examine the effects of excessive sugar consumption on both weight gain and gum disease, emphasizing the need for dietary modifications.
Impact of Refined Carbohydrates: Discuss the role of refined carbohydrates in promoting inflammation and its connection to gum disease, emphasizing the importance of balanced diet choices.
B. Balanced Diets for Optimal Gum Health:
Nutritional Recommendations: Present insights from dietitians on a balanced diet that promotes excellent gum health, encompassing essential nutrients like vitamin C, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants.
Mediterranean Diet and Gum Health: Analyze the potential benefits of the Mediterranean diet on both body weight and gum health, emphasizing the role of anti-inflammatory foods.
IV. Addressing Diverse Perspectives:
A. Cultural Considerations:
- Exploring Cultural Differences: Discuss how diverse cultural practices and dietary habits may influence the weight-gum disease relationship, highlighting examples from different regions of the world.
- Disparities in Access to Nutritious Food: Shed light on the impact of socioeconomic factors on availability and affordability of nutritious foods, potentially affecting gum health.
B. Individual Variations:
- Genetic Predisposition: Examine the role of genetic factors in both weight management and susceptibility to gum disease, calling for further research in this area.
- Personal Hygiene Habits: Discuss the potential combined effects of weight and oral hygiene practices on gum health, encouraging awareness and proper dental care practices.
Conclusion:
Understanding the intricate connection between weight and gum disease is pivotal in enhancing oral health outcomes. By delving into relevant statistics, exploring insights from dietitians, and considering diverse perspectives, this article has shed light on the invaluable relationship between weight and gum disease. Encouraging a balanced diet, maintaining proper oral hygiene, and seeking professional dental care are essential steps in preventing and managing gum disease effectively.
Sources
- Global burden of untreated caries, a systematic review and metaregression
- Effect of diet and nutrition on oral health, An overview of systematic reviews
- Healthy food subsidies and unhealthy food taxation, A systematic review of the evidence
- Periodontal systemic associations, review of the evidence